Denmark Strait Cataract
A hidden force beneath the ocean’s surface dwarfs every land-based waterfall. The Denmark Strait cataract plunges over 11,500 feet, driving powerful currents that shape marine life and climate. Something we’ll get into more within the piece.

An Underwater Behemoth That Breaks Records
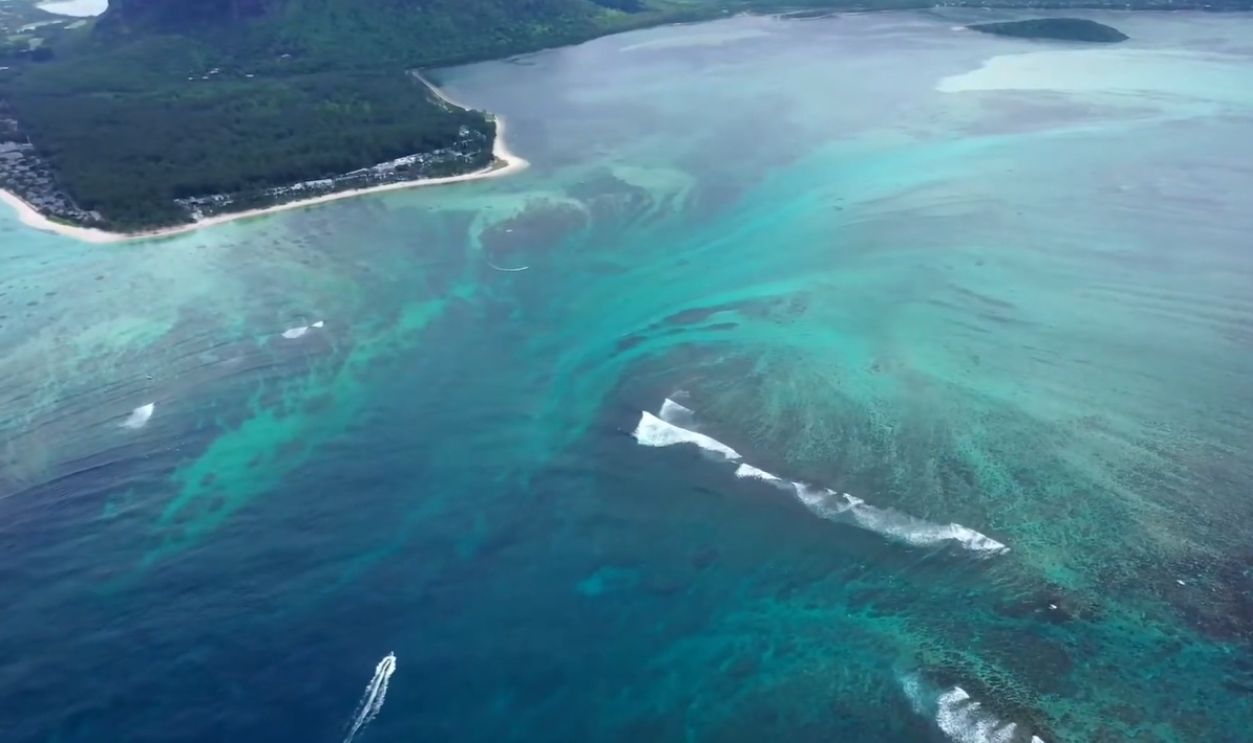
The Denmark Strait cataract isn’t just massive—it’s the largest waterfall on Earth. Unlike any terrestrial cascade, it plunges 11,500 feet, a descent so extreme it would engulf three Burj Khalifas stacked atop one another. It transports millions of cubic feet per second, which surpasses the volume of any surface waterfall.
 Denmark Strait Cataract, The Largest Waterfall In The World | WHOA AMAZING! by WHOA AMAZING!
Denmark Strait Cataract, The Largest Waterfall In The World | WHOA AMAZING! by WHOA AMAZING!
More Powerful Than 1000 Niagaras
By comparison, Niagara Falls moves about 85,000 cubic feet of water per second. The Denmark Strait cataract? An astounding 175 million cubic feet per second. That’s over 2000 times the volume, which makes every celebrated waterfall on land seem minuscule in contrast.
 Mhsheikholeslami, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Mhsheikholeslami, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Shaped By Nature’s Unseen Forces
Underwater waterfalls don’t develop like their land-based counterparts. Instead of erosion sculpting rock, temperature and salinity variations drive this phenomenon. Cold Arctic water, denser than the warm Atlantic, dives down an invisible precipice, which generates an immense, unstoppable current deep beneath the surface.
 Denmark Strait Cataract, The Largest Waterfall In The World | WHOA AMAZING! by WHOA AMAZING!
Denmark Strait Cataract, The Largest Waterfall In The World | WHOA AMAZING! by WHOA AMAZING!
Detected Through Sonar
For centuries, no one knew it was there. In the late 20th century, oceanographers employed sophisticated sonar mapping to identify dramatic temperature shifts in the Denmark Strait. This led to the remarkable discovery of an underwater cascade far surpassing any found on land. Science had redrawn geography.
 NOAA Photo Library, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
NOAA Photo Library, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
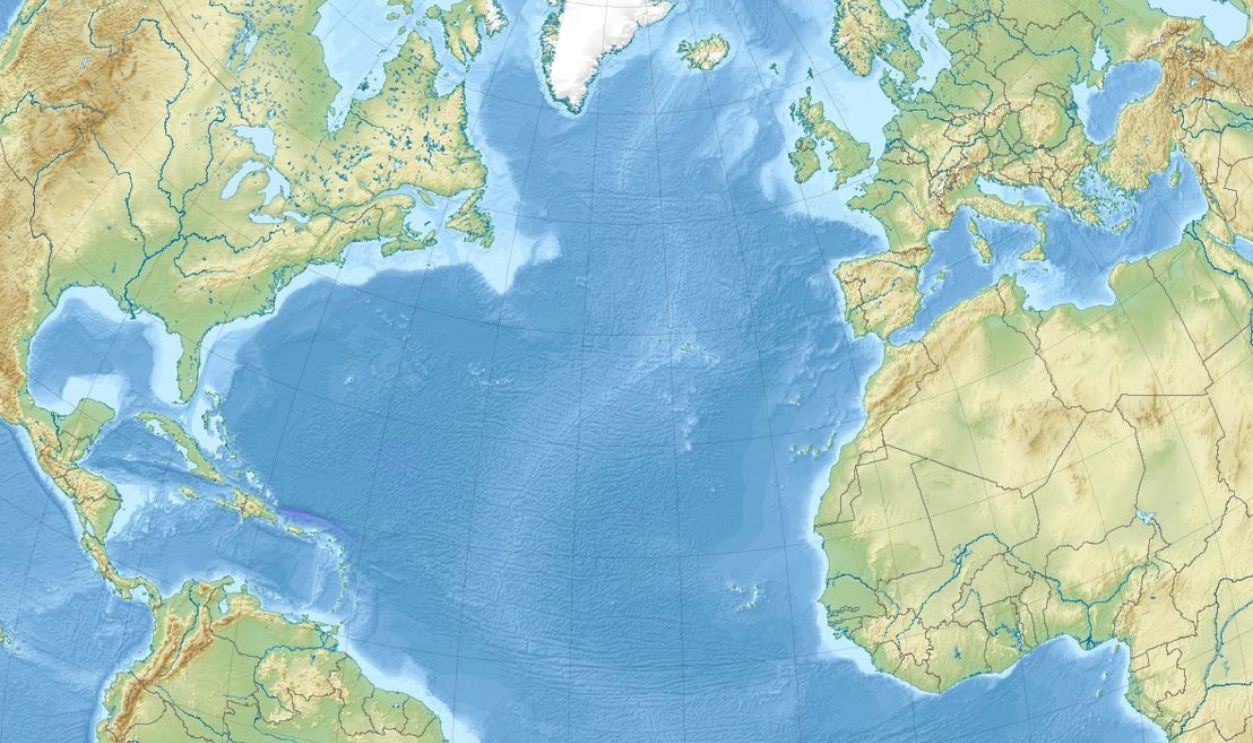
Surpassing Landmarks In Magnitude
Spanning 300 miles across, the Denmark Strait cataract eclipses even the Grand Canyon in width. Satellites can even map their temperature and salinity changes. This natural marvel stretches across a vast oceanic divide, making it one of Earth’s most extraordinary concealed vistas.
 Niagara66, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Niagara66, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
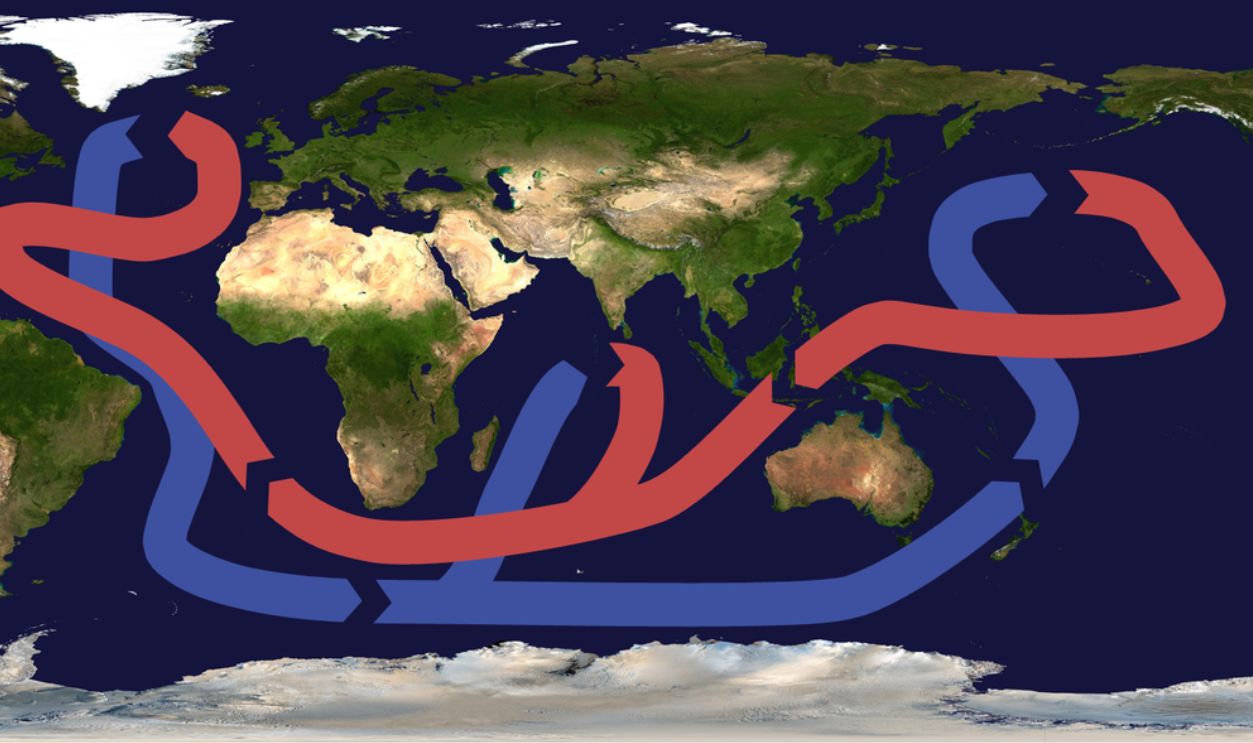
Important For Global Ocean Circulation
The Earth’s climate relies on deep-sea currents, and this waterfall is an essential component of the system. By fueling thermohaline circulation, it helps disperse heat worldwide. Without it, tropical regions would overheat while northern latitudes would freeze, which would disturb Earth’s climatic equilibrium.
 Explore the World’s largest Under Water Falls! Denmark Strait! by Explore
Explore the World’s largest Under Water Falls! Denmark Strait! by Explore
A Legacy Of The Last Ice Age
Ancient glaciers molded the seafloor thousands of years ago, which allows dense Arctic waters to descend into deep ocean basins. This submerged waterfall is a direct remnant of the Ice Age, a proof of a time when colossal ice sheets dominated the northern hemisphere.
 Christine Zenino from Chicago, US, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Christine Zenino from Chicago, US, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Colder Than Antarctic Waters
Water cascading down the Denmark Strait cataract is frigid and frequently nears -2°C (28°F). Unlike warm waterfalls that generate mist and rainbows, this one remains undetectable, confined to the bone-chilling abyss of the North Atlantic, beyond human reach and perception.
 Uwe Dedering, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Uwe Dedering, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
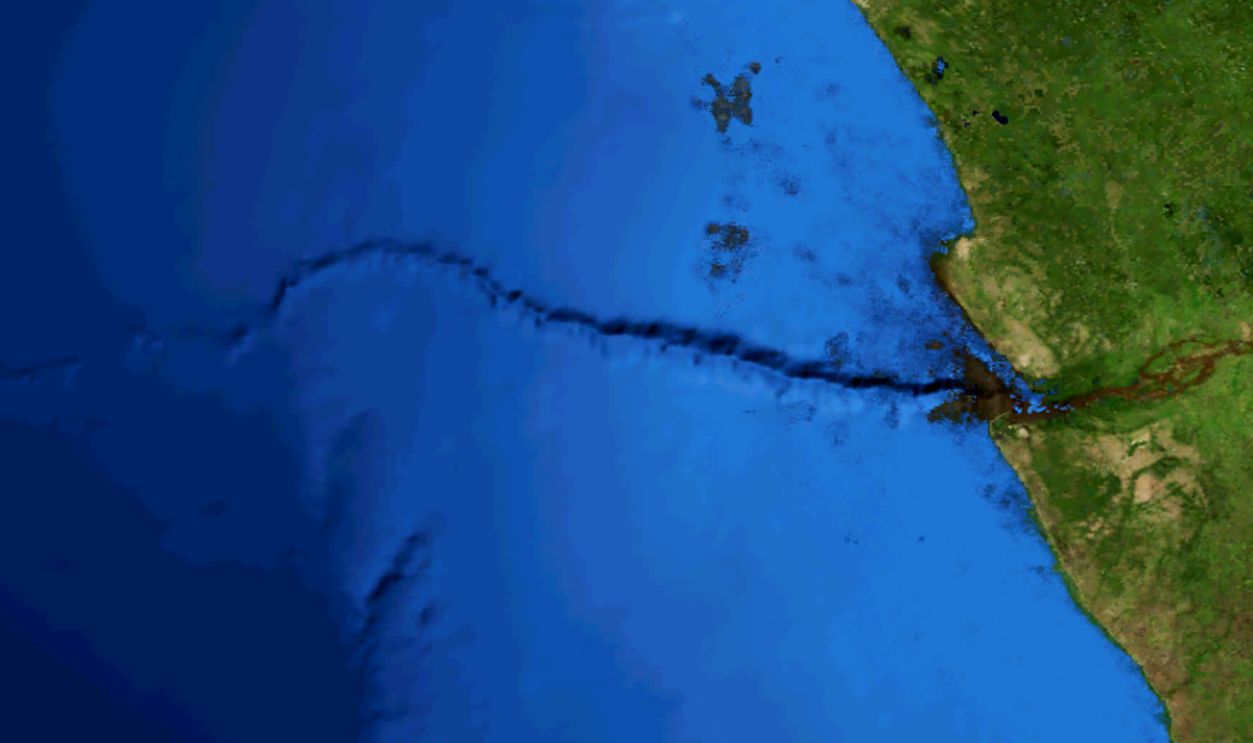
Silently Reshaping The Ocean Floor
Its overwhelming force sculpts deep channels and submarine valleys, perpetually altering the seafloor. Researchers have uncovered evidence of vast trenches eroded by the persistent movement of these currents. It’s true; water alone can carve sceneries as dramatically as wind and rock.
 Mikenorton, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Mikenorton, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
A Submerged Wonder Beyond Human Exploration
Due to its extreme depth and treacherous conditions, including freezing temperatures and immense pressure, even the most advanced underwater exploration technologies struggle to explore the Denmark Strait cataract. This leaves many of its mysteries still unknown and unexplored.
 Richard Varcoe, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Richard Varcoe, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
No Human Has Ever Witnessed It Firsthand
Even with modern advancements, no diver or submersible has ever fully examined the Denmark Strait cataract. The extreme depth, freezing waters, and immense pressure render it one of Earth’s most inaccessible natural wonders, concealed in darkness beyond human reach.
The Great Conveyor Belt’s Driving Force
Scientists consider this waterfall a vital part of the global conveyor belt, an immense ocean current system circulating warm and cold waters worldwide. Without it, weather patterns would shift unpredictably and disrupt marine ecosystems and even agricultural cycles on a global scale.
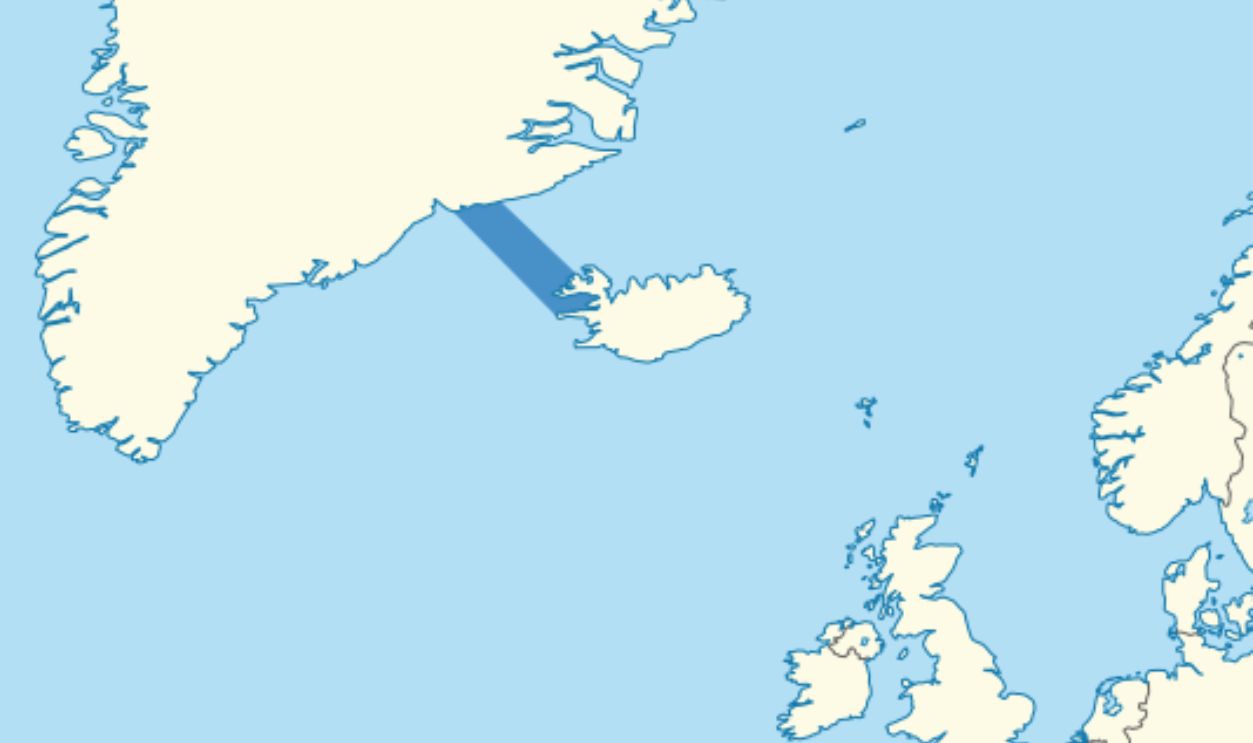
Forms An Invisible Boundary Between Oceans
Where the cold Arctic meets the warmer Atlantic, an unseen barrier emerges. The Denmark Strait cataract reinforces this separation, which ensures Arctic waters remain distinct from the Atlantic. This, in turn, influences everything from fish migration to hurricane formation.
 Aplaice, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Aplaice, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
A Hidden Haven For Deep-Sea Life
As nutrient-rich waters plunge downward, they create an oasis for marine organisms in the ocean depths. From microscopic plankton to deep-sea fish, entire ecosystems rely on the perpetual mixing of cold and warm waters generated by this unseen powerhouse.
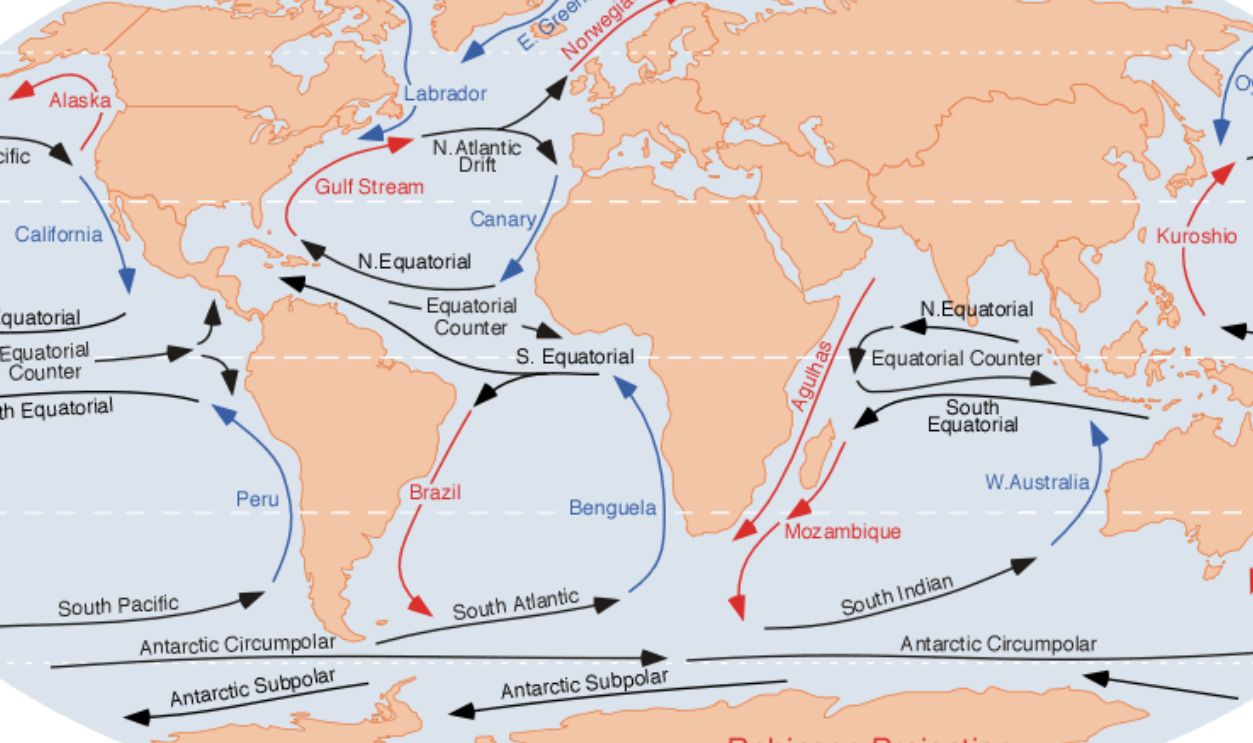
Stronger Than Some Ocean Currents
While the Gulf Stream is famous for transporting warm waters across the Atlantic, the Denmark Strait cataract exerts an even greater force in the deep ocean. It plays an important role in the regulation of deep-sea currents that sustain Earth’s oceans, feeding all of marine biodiversity.
 Dr. Michael Pidwirny, Wikimedia Commons
Dr. Michael Pidwirny, Wikimedia Commons
Unaffected By Surface Erosion
Unlike terrestrial waterfalls, which change over time due to wind and shifting rock, the Denmark Strait cataract remains largely unaltered. As long as cold Arctic waters continue to flow, this deep-sea cascade will persist and likely flow for millions of years into the future.
 MEDIACRAT, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
MEDIACRAT, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
A Key Player In Oceanic Mixing
The Denmark Strait cataract is more than just a waterfall; as we have already mentioned, it is a mixer of cold Arctic waters with warmer Atlantic currents. This mixing helps stabilize ocean temperatures and salinity, which in turn has a direct impact on marine ecosystems and global climate patterns.
 Brisbane, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Brisbane, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
A Natural Wonder That Outlasts Civilization
Long before humans developed an understanding of ocean currents and their global significance, the Denmark Strait cataract had already been shaping Earth’s climate and ocean systems for thousands of years. It is likely to remain one of nature’s most powerful and hidden forces for millennia to come.
 Denmark Strait Cataract, The Largest Waterfall In The World | WHOA AMAZING! by WHOA AMAZING!
Denmark Strait Cataract, The Largest Waterfall In The World | WHOA AMAZING! by WHOA AMAZING!
Deflection Due To Coriolis Effect
As a result of the Coriolis effect (the deflection of moving objects caused by Earth’s rotation), the downward flow of water in the Denmark Strait Cataract is redirected to the right. So, the descending water on the Greenland side is approximately 1 kilometer higher than on the opposite side.
 NASA/GSFC, MODIS Rapid Response Team, Jacques Descloitres, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/GSFC, MODIS Rapid Response Team, Jacques Descloitres, Wikimedia Commons
Its Power Could Reshape Future Climate Trends
As global temperatures fluctuate, changes in the Denmark Strait cataract could significantly disrupt oceanic currents. Such alterations in the deep-sea cascade could trigger unexpected climatic consequences worldwide, which can include shifts in weather patterns and sea levels.
Sound Propagation In Water
The Denmark Strait’s temperature and salinity gradients create water layers that affect sound speed and propagation. These variations influence sonar performance and underwater communication, as sound waves bend due to density differences, it impacts submarine operations and detection in the region.
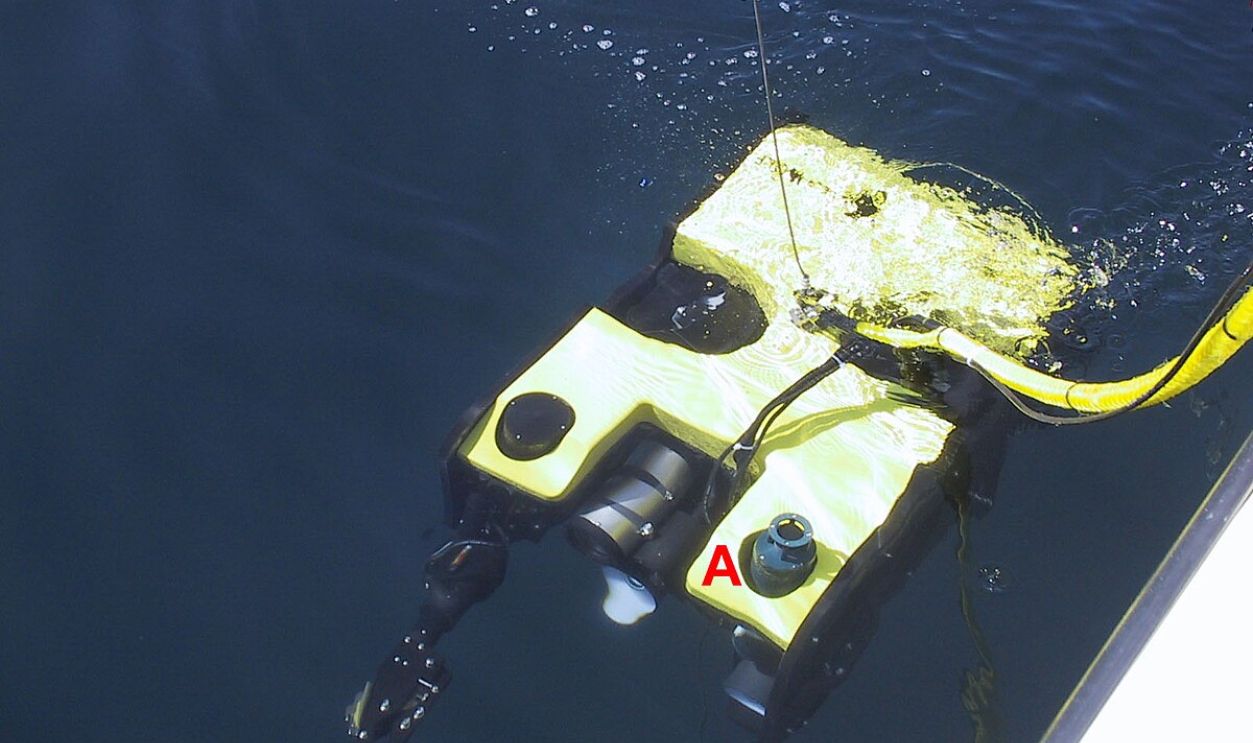
Technological Advancements In Acoustic Monitoring
Advancements in acoustic monitoring technologies, including the use of ADCPs and seismic oceanography, have enhanced the ability to observe and understand the complex dynamics of the Denmark Strait, which aids submarine exploration and communication.
 J.R. Lacy, USGS Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center, Wikimedia Commons
J.R. Lacy, USGS Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center, Wikimedia Commons
Spatial And Temporal Overflow Structure
Since 1999, scientists have deployed an array of bottom-mounted acoustic instruments in the Denmark Strait to measure current velocity, overflow transport, and bottom-to-surface acoustic travel times. These instruments have revealed fluctuations in the Denmark Strait Overflow, including seasonal variations and episodic pulses of dense water moving southward.
 Desertstar, CC BY 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Desertstar, CC BY 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Influence Of Storm Events On Overflow Pulse Events
Recent acoustic monitoring has demonstrated that extreme weather conditions, such as intense storms in the region, can trigger rapid pulses of dense water flowing through the Denmark Strait. These storm-driven pulses can significantly alter overflow transport patterns and have consequences for deep ocean circulation.
One Of Earth’s Least Known Mega-Structures
Despite its staggering size and immense impact on global ocean currents, the Denmark Strait cataract is rarely mentioned outside scientific circles. This makes it one of the planet’s most significant yet largely overlooked natural wonders, hidden from broader public awareness despite its vital role in Earth’s climate system.














