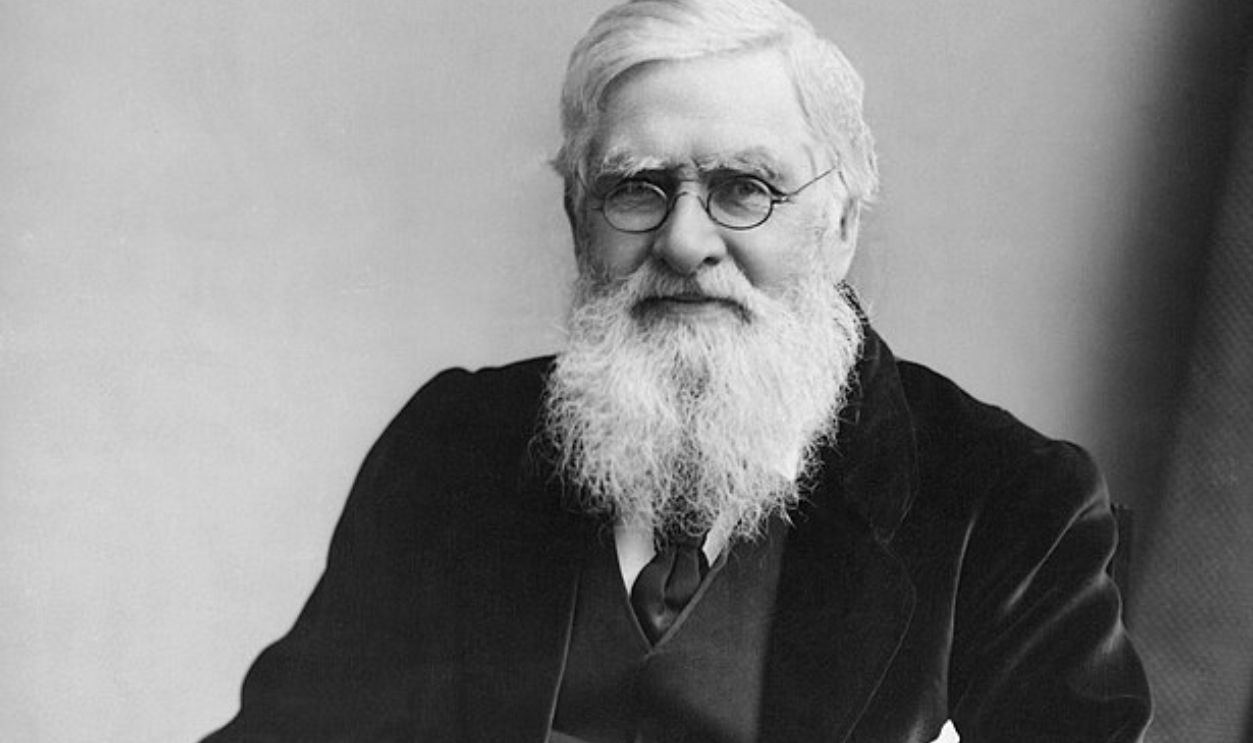
The Wallace Line’s Hidden Link to Biodiversity
An invisible line passes through the Malay Archipelago, separating two unique ecosystems where distinct species on either side thrive. So, what is the Wallace line, and what secrets does it hide?

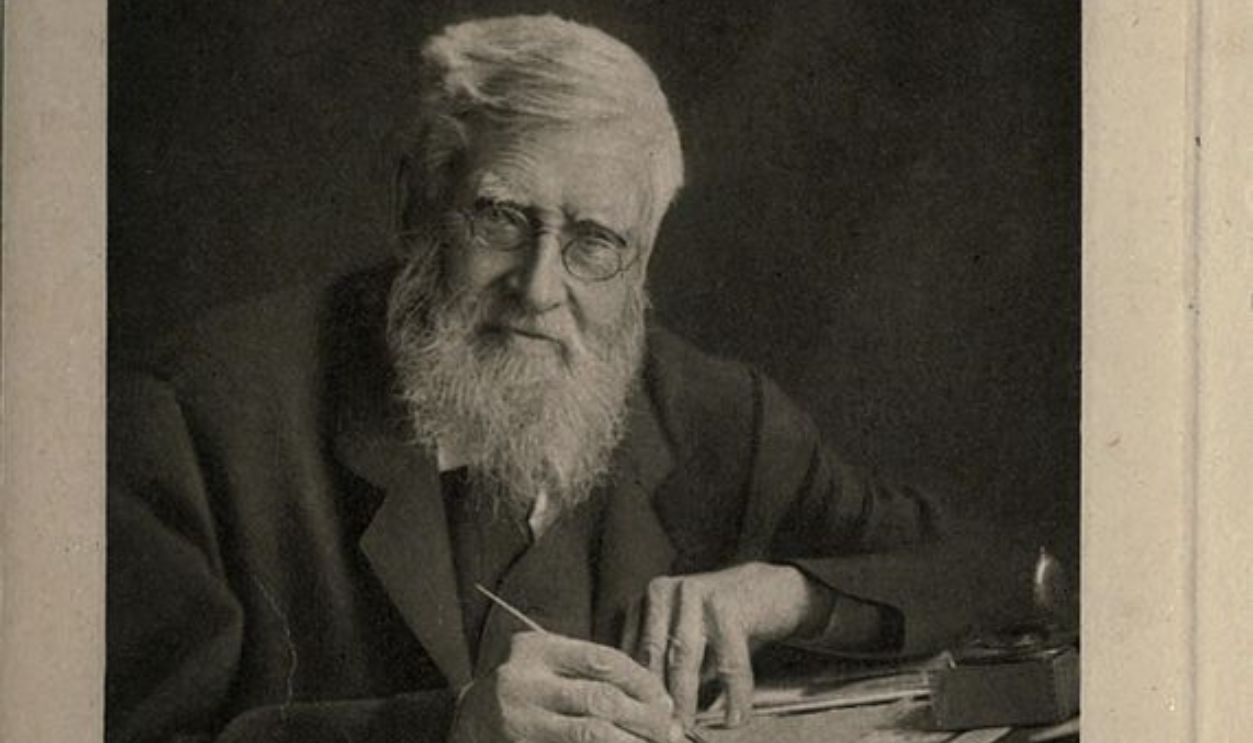
Alfred Russel Wallace And His Discoveries
Alfred Russel Wallace, a British naturalist and explorer, discovered the Wallace Line while studying species distribution in the Malay Archipelago. Wallace is well-regarded for his contributions to the theory of natural selection alongside Darwin, but he also pioneered biogeography by documenting how species varied dramatically across regions.
 London Stereoscopic and Photographic Company, Wikimedia Commons
London Stereoscopic and Photographic Company, Wikimedia Commons
Critical Observations In Evolutionary Biology
His studies in the 1850s highlighted a sharp distinction between Asian and Australian species, which he later attributed to ancient geological separations. His observations laid the groundwork for evolutionary biology, demonstrating how geographic boundaries could lead to diverse ecosystems and species evolution.
 Marchant, James, Wikimedia Commons
Marchant, James, Wikimedia Commons
Origins Of The Wallace Line Concept
The concept of the Wallace Line originated during Wallace's exploration of Southeast Asia, where he noticed that species abruptly changed across specific geographic points. Unlike Darwin's gradual evolutionary processes, Wallace's theory emphasized geographic isolation as a key driver of biodiversity.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Even Invisible Barriers Impact Evolution
He proposed the Wallace Line in the mid-19th century to show the differences in animal life between regions, and his work influenced scientific approaches to biogeography. Wallace's insights were foundational, showing how even invisible barriers could profoundly impact species distribution and evolutionary history.
 Anniewongw, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Anniewongw, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
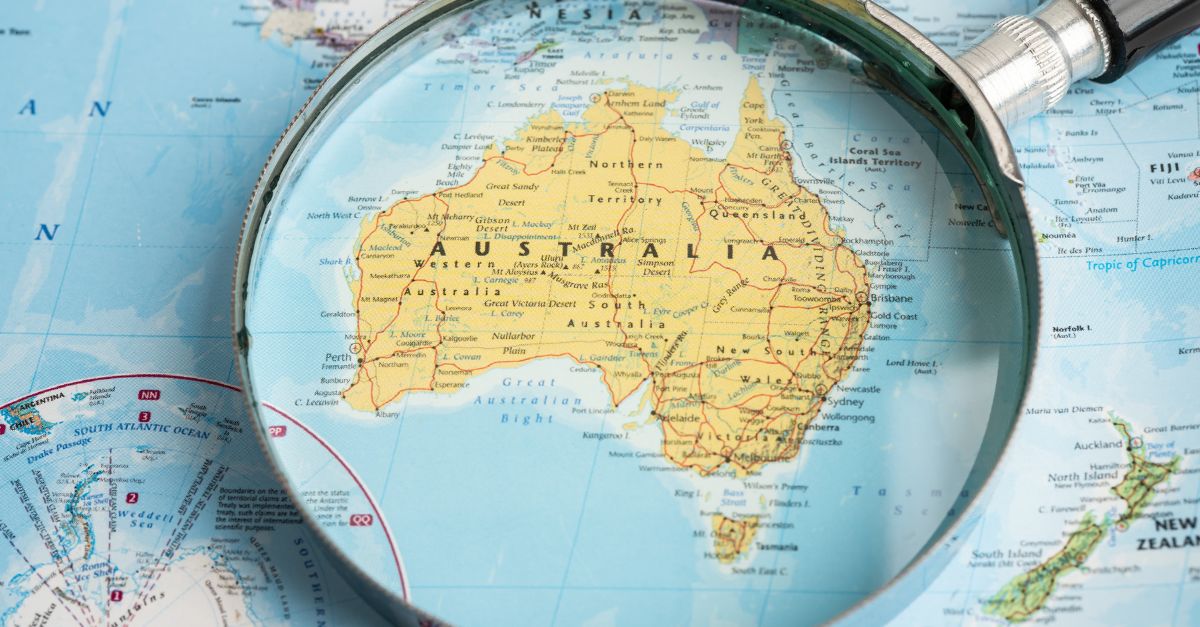
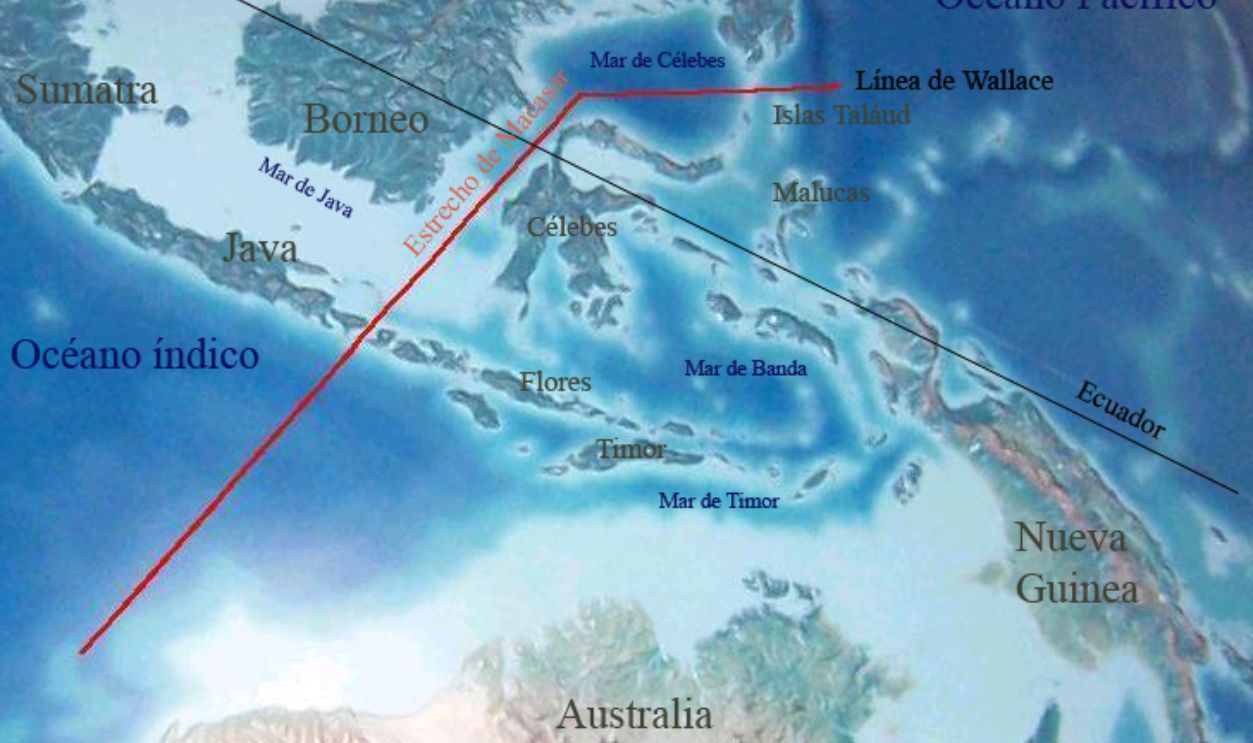
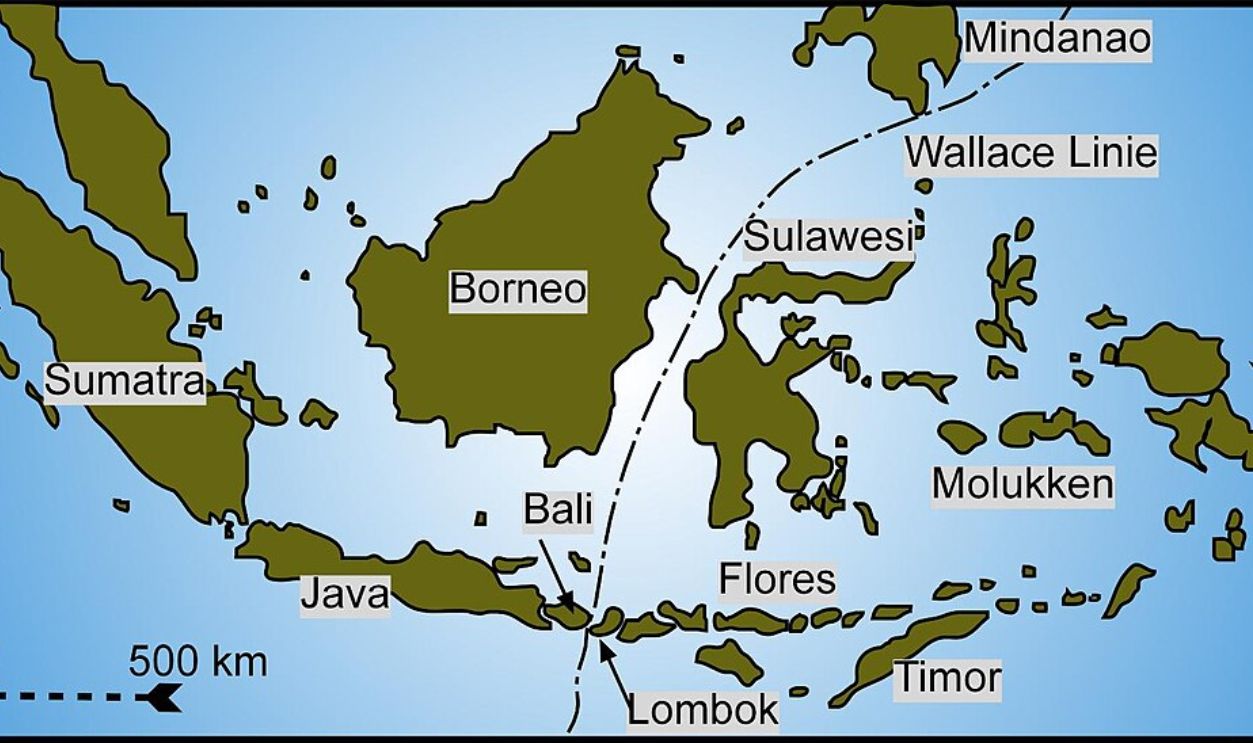
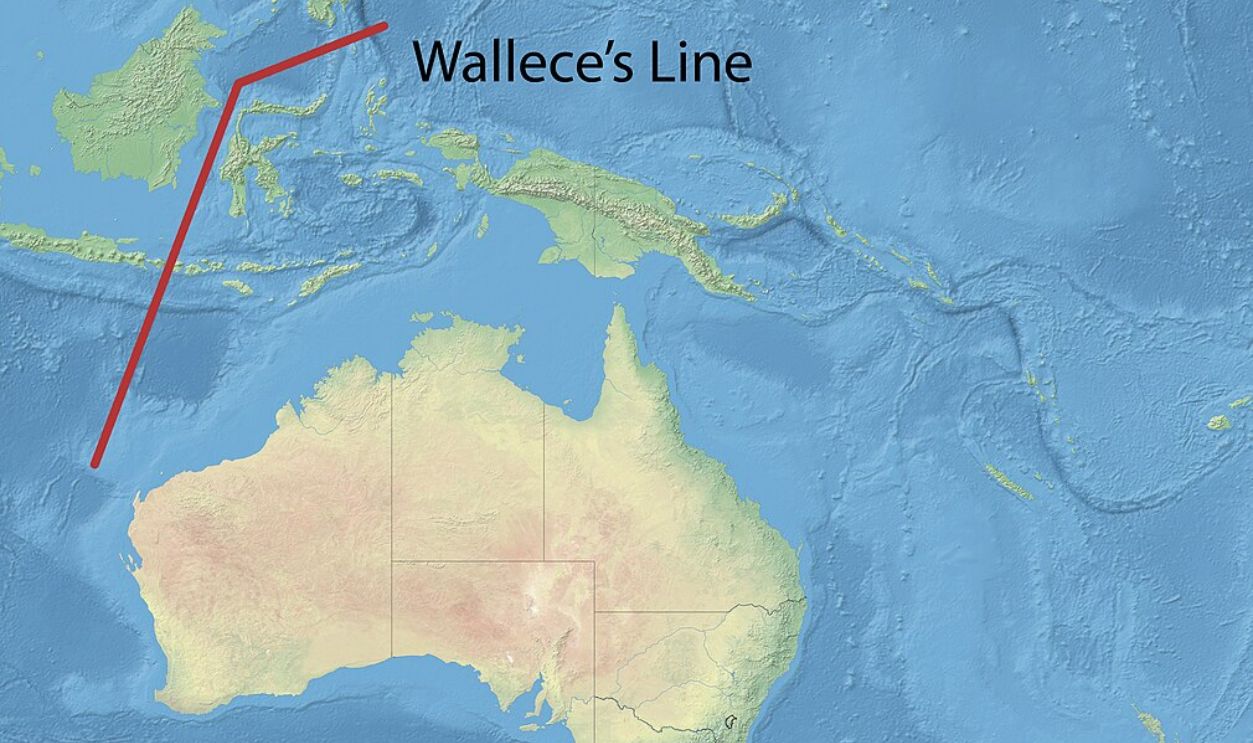
The Wallace Line And Its Geographic Location
The Wallace Line is a remarkable biogeographic boundary separating the fauna of Asia and Australia. Stretching through Indonesia between Bali and Lombok, this line outlines distinct animal communities on either side—Asian fauna such as tigers and elephants on one, and unique Australian species like marsupials on the other.
 Gunnar Ries, CC BY-SA 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
Gunnar Ries, CC BY-SA 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
Two Biodiversities
The line's influence is visible within just a few miles of the sea, making it a stark natural boundary in biodiversity. Proposed by Alfred Russel Wallace in 1859, this line remains essential in understanding the biological and geological forces shaping biodiversity across Asia and Australia.
 Till Niermann, CC BY 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Till Niermann, CC BY 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
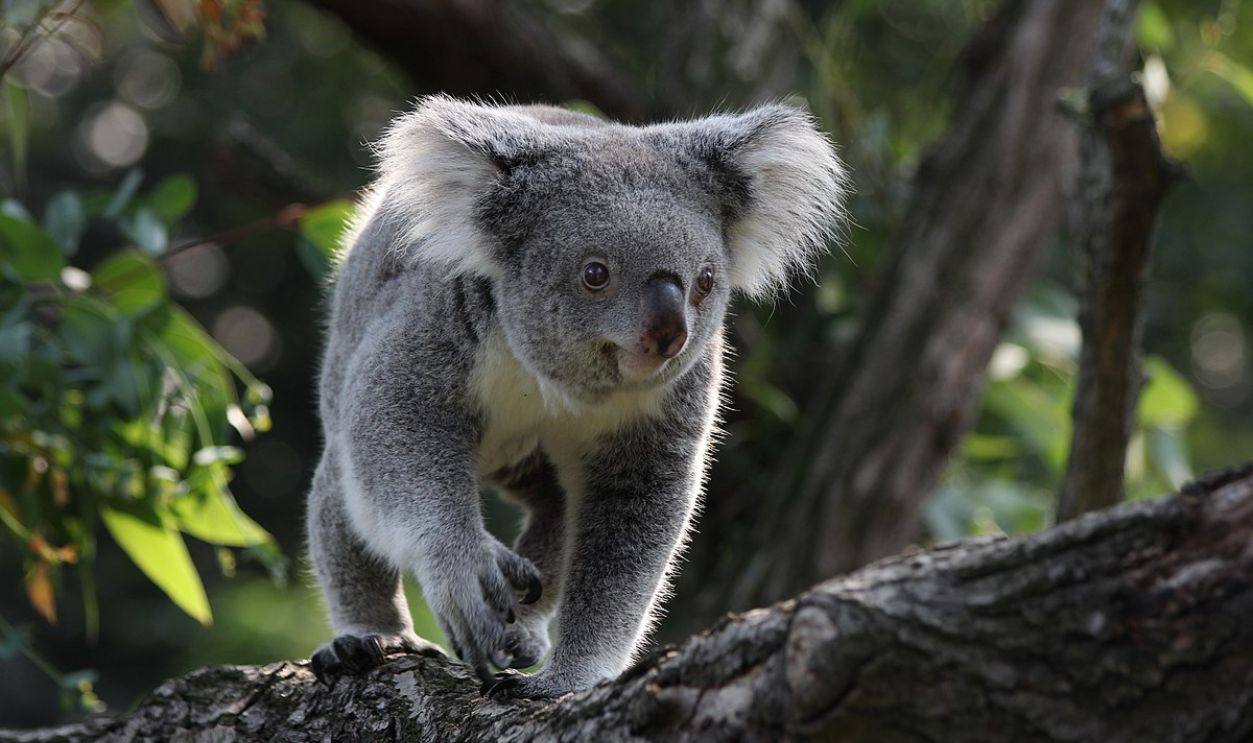
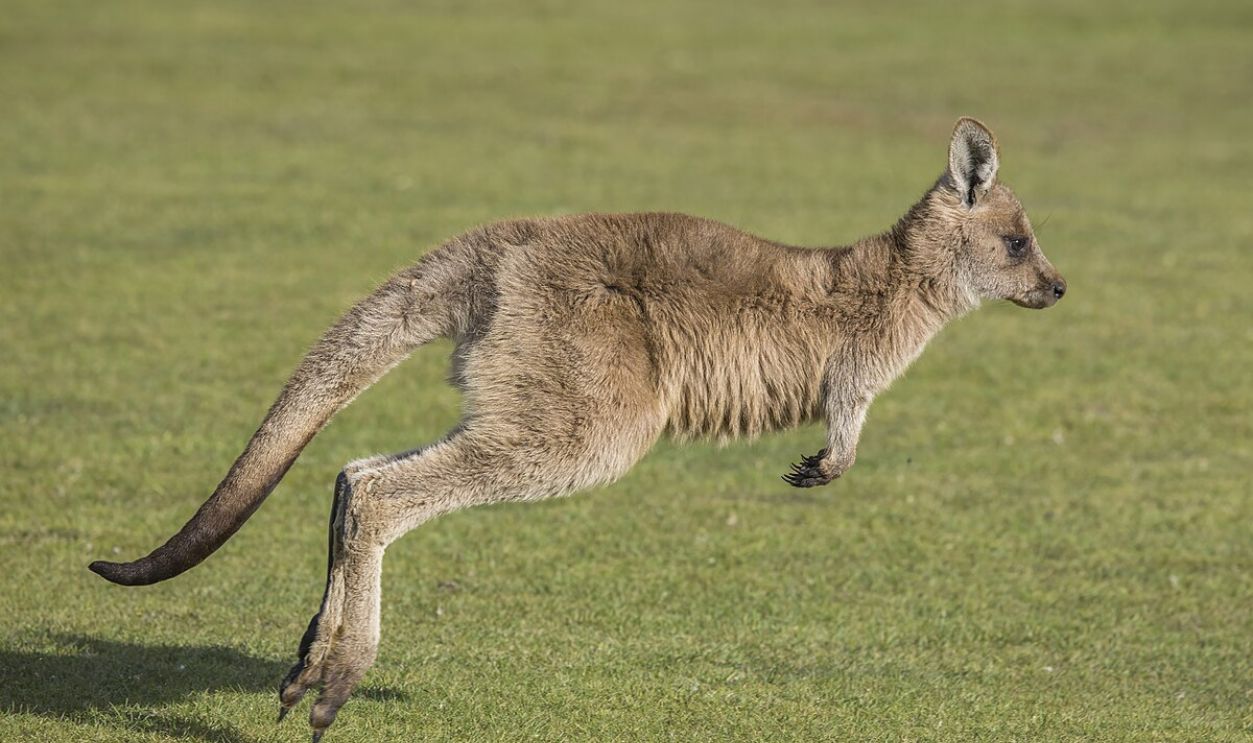
It Differentiated Animal Life In Asia And Australia
The Wallace Line outlines two drastically different ecosystems, with Asian species, such as elephants, tigers, and apes, dominating the west and Australian species, like kangaroos, cockatoos, and marsupials, thriving to the east. This striking division reflects millions of years of isolation caused by deep oceanic waters that once separated lands.
 Charles J. Sharp, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Charles J. Sharp, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
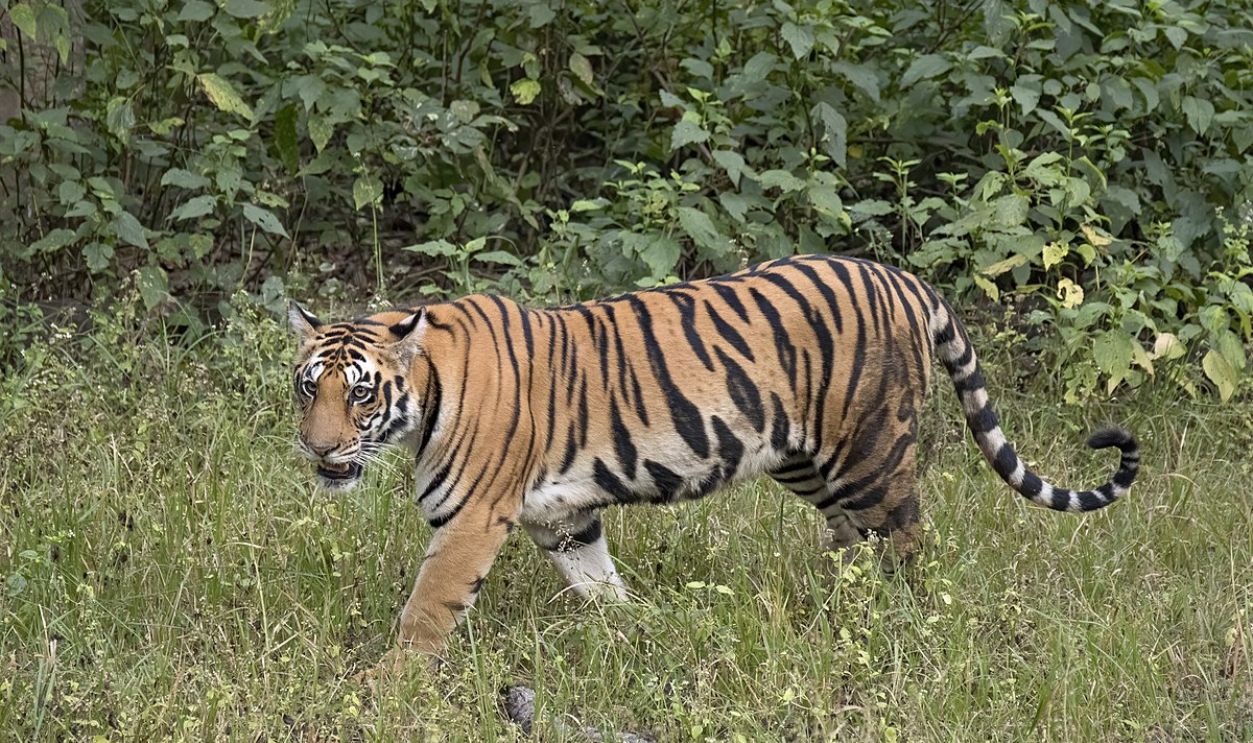
Species Distribution
Today, these physical barriers continue to prevent many animals from crossing the line, enforcing unique evolutionary paths on either side. Wallace's observations of these distinctions laid the foundation for understanding species distribution and biogeographic boundaries. In short, they explain that the geological past shapes the biological present.
 Charles J. Sharp, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Charles J. Sharp, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
It's Most Noticeable Between Bali And Lombok
Nowhere is this line more apparent than between the Indonesian islands of Bali and Lombok, separated by 32 kilometers across the Lombok Strait. This narrow strip of water represents a major faunal divide. Species typical of Asia are found in Bali, while Lombok has species akin to those of Australia.
 listfiles/Kanguole, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
listfiles/Kanguole, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
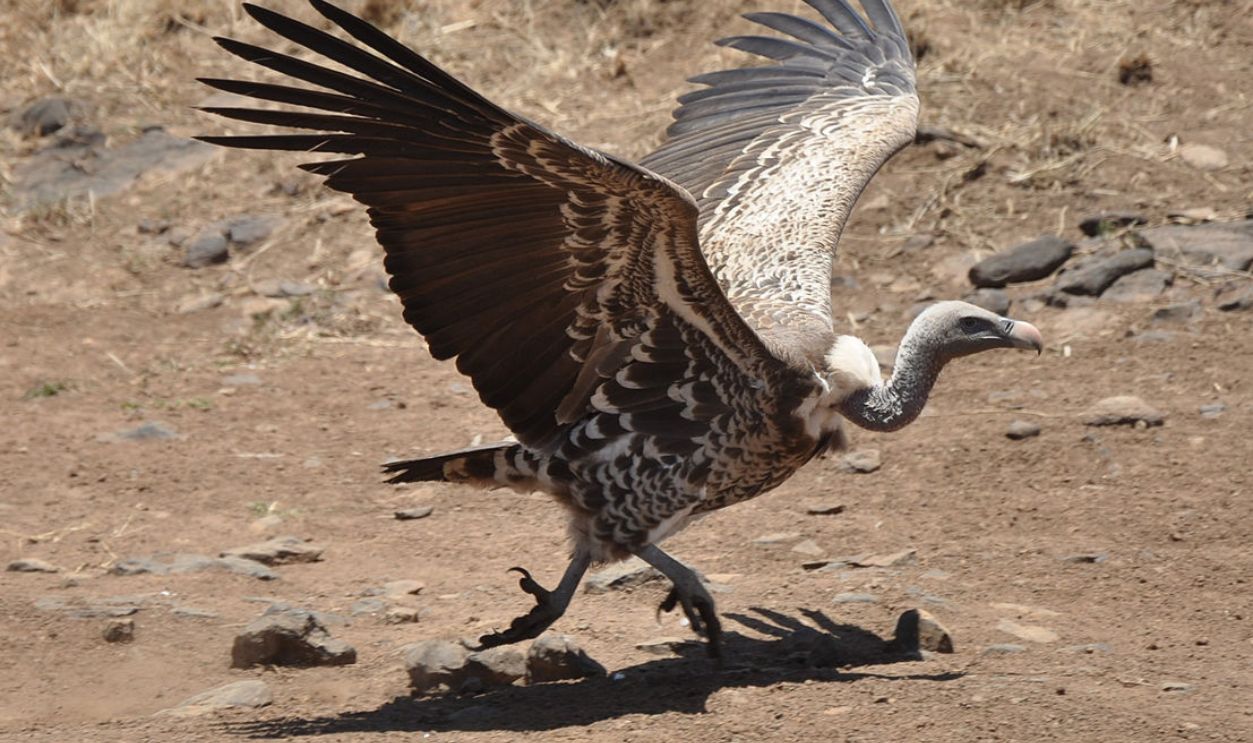
Even Applies To Birds
Even birds and insects, which could seemingly cross this short distance, tend to remain confined to either side. This distinct boundary highlights the ecological impact of natural barriers, underscoring Wallace's observation that seemingly minor geographic separations can significantly influence biodiversity.
 Gyps, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Gyps, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
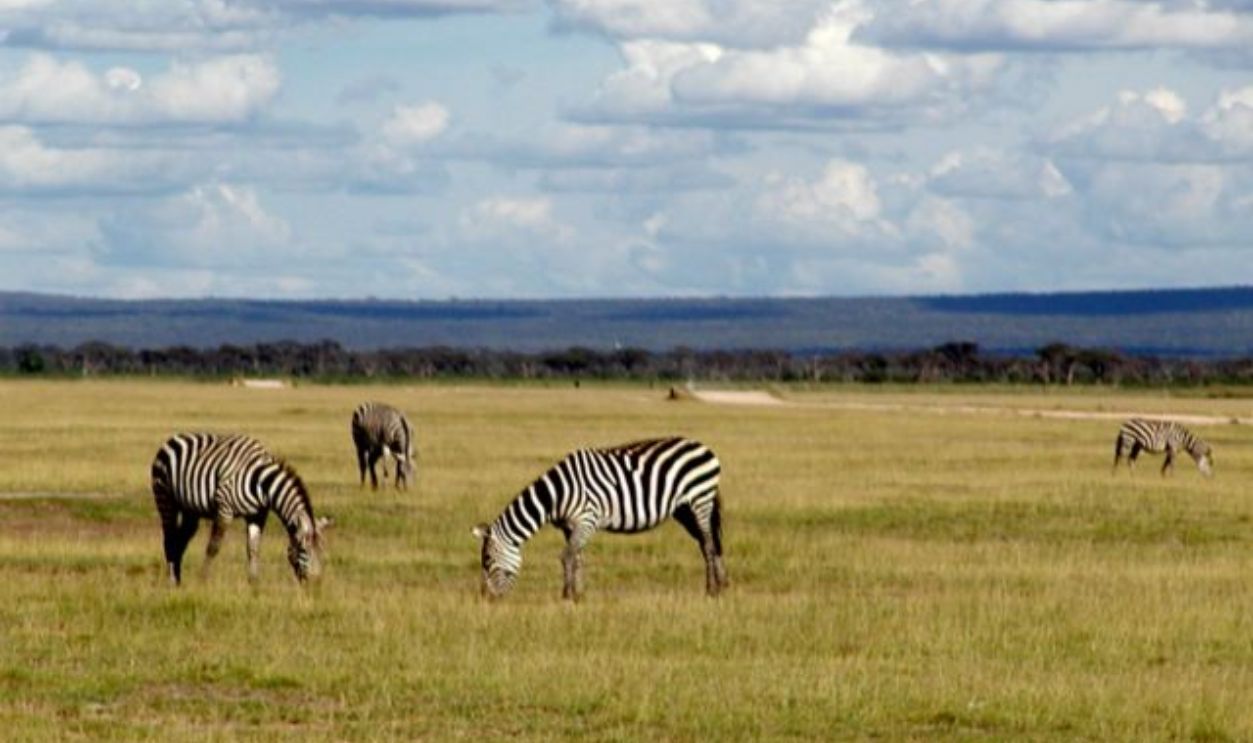
Wallace Explained How Biogeographic Boundaries Affect Ecosystems
Biogeographic boundaries like the Wallace Line act as barriers that guide the distribution and evolution of species. These boundaries can restrict movement, allowing isolated ecosystems to develop unique characteristics over time. In this case, it was deep ocean trenches that prevented species from migrating across.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
The Role Of Geographic Factors
This separation has implications for evolutionary biology, helping scientists study how geographical barriers contribute to speciation, ecosystem diversity, and regional endemism. These natural divisions show the role of geographic factorsin shaping ecosystems with their unique living creatures.
 Diliff, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Diliff, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
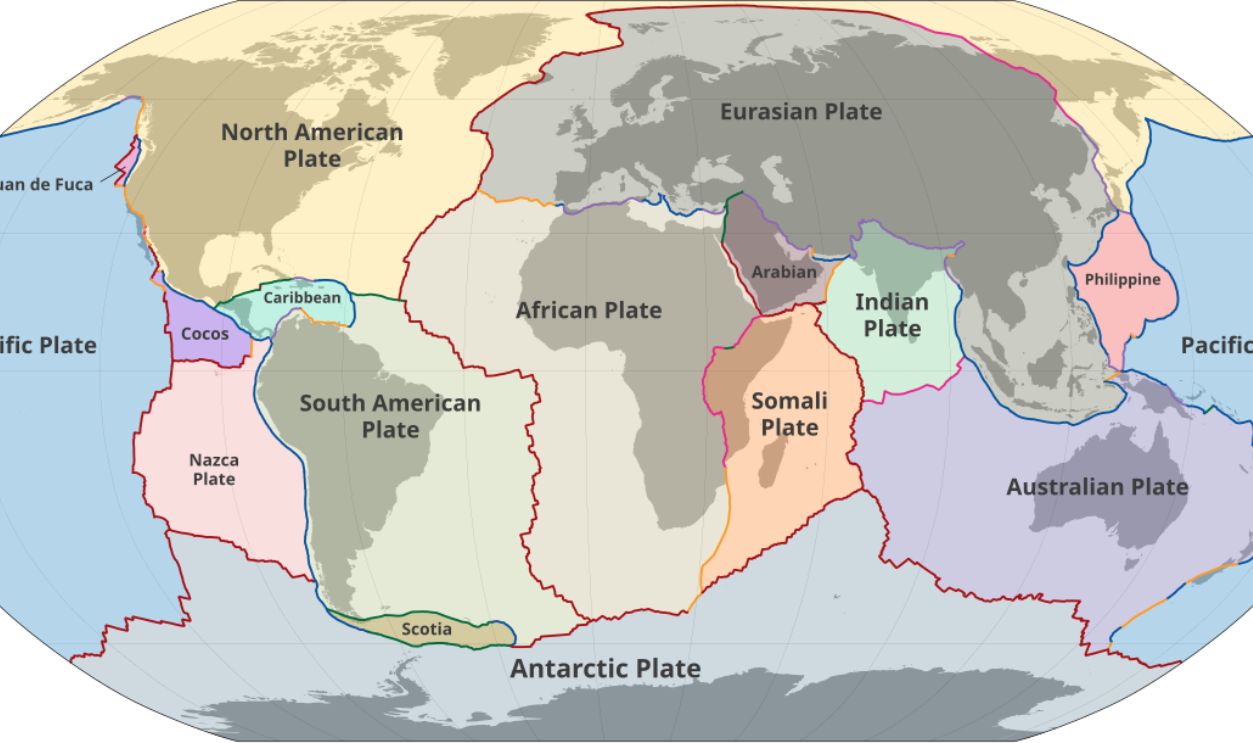
Plate Tectonics Helped Shape The Wallace Line
Plate tectonics played a huge role in the creation of the Wallace Line due to the separation of landmasses that once allowed species to intermingle. The line corresponds to ancient tectonic activity that split the Australian and Asian plates, leading to deep sea channels that continue to restrict species movement.
 M.Bitton, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
M.Bitton, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Basis Of Wallace's Observations
This tectonic history established a lasting boundary between the faunal regions, creating the basis for Wallace's observations and contributing to the unique ecosystems found on either side of the line today. However, this concept became widely accepted in the 1960s—several decades after Wallace passed away.
 Hughrance, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Hughrance, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
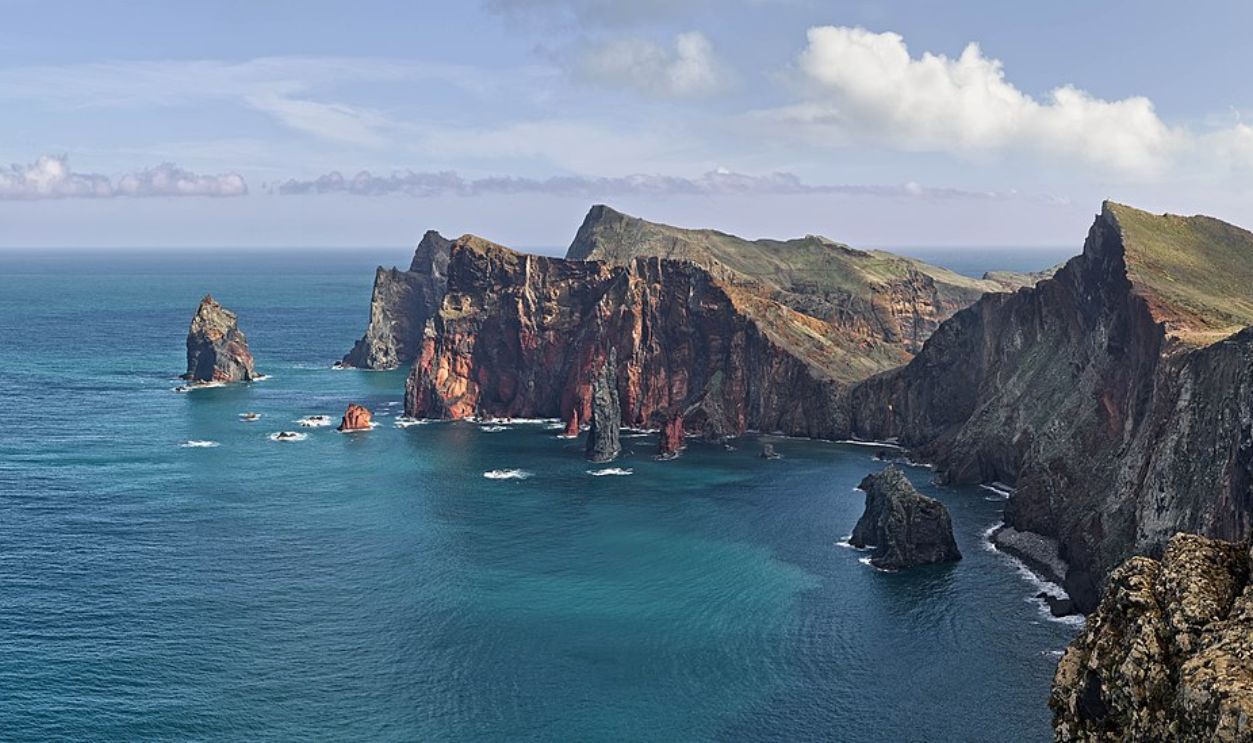
Early Theories Behind Biogeography
Biogeography, or the study of species distribution across geographic regions, gained scientific attention in the 19th century, driven by Wallace's observations. Before then, scientists had only vaguely considered how geography influenced biodiversity. Wallace's studies in the Malay Archipelago demonstrated that geographic boundaries like oceans could act as natural separators.
 Richard Bartz, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Richard Bartz, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
One Of The Founders Of The Field
Wallace's work paved the way for future biogeographic studies, making him one of the founders of the field. His observations inspired further research on geographic isolation and environmental pressures shaping ecosystems, concepts still central to evolutionary biology today.
 Alejandro Sanchez Ortiz, Shutterstock
Alejandro Sanchez Ortiz, Shutterstock
Why Is The Wallace Line Both Real And Imaginary?
The Wallace Line is a fascinating paradox—it is invisible yet impactful. Despite being an imaginary boundary, it details a stark biological difference between Asia and Australia. Species on either side of the line differ due to ancient geological separations that left oceanic trenches acting as biological barriers.
 Nrg800, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Nrg800, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Invisible Ecological Boundaries
Though no physical wall exists, this line still influences which species thrive where, as seen in the distinct mix of native species on one side and a different one on the other. It serves as a reminder of how invisible ecological boundaries can profoundly impact biodiversity over millennia.
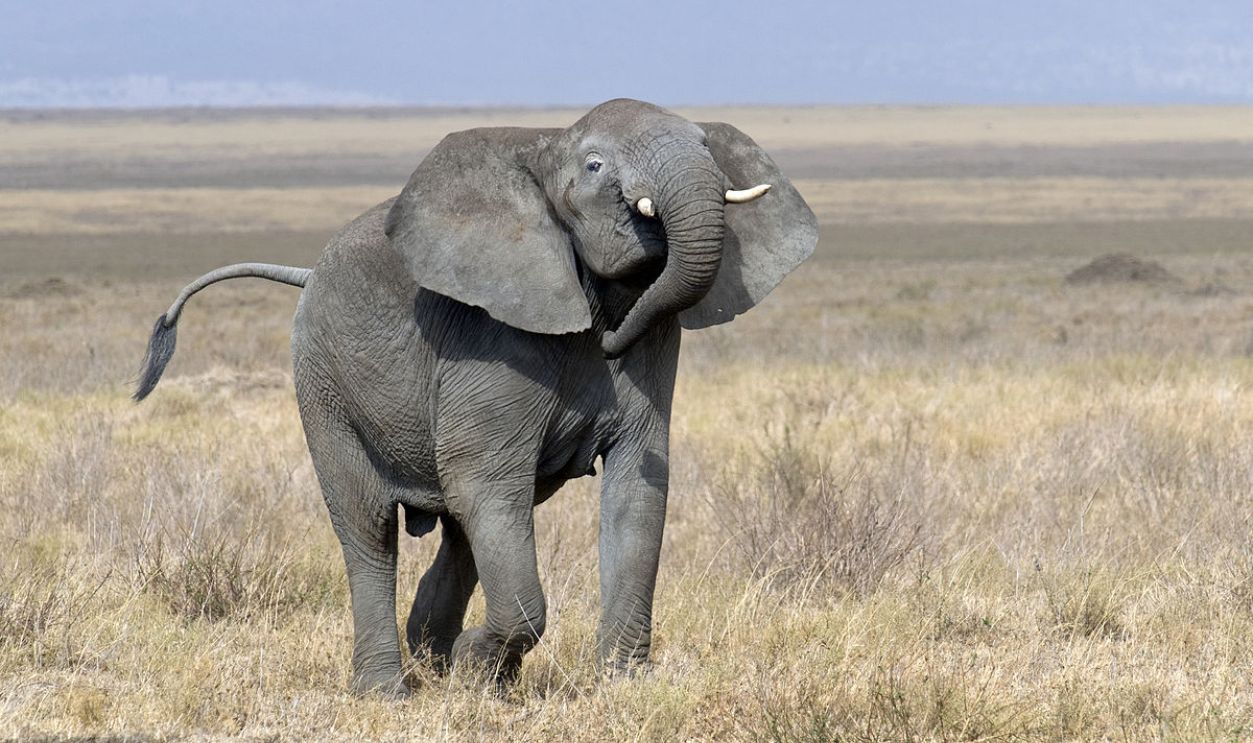 Yathin S Krishnappa, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Yathin S Krishnappa, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
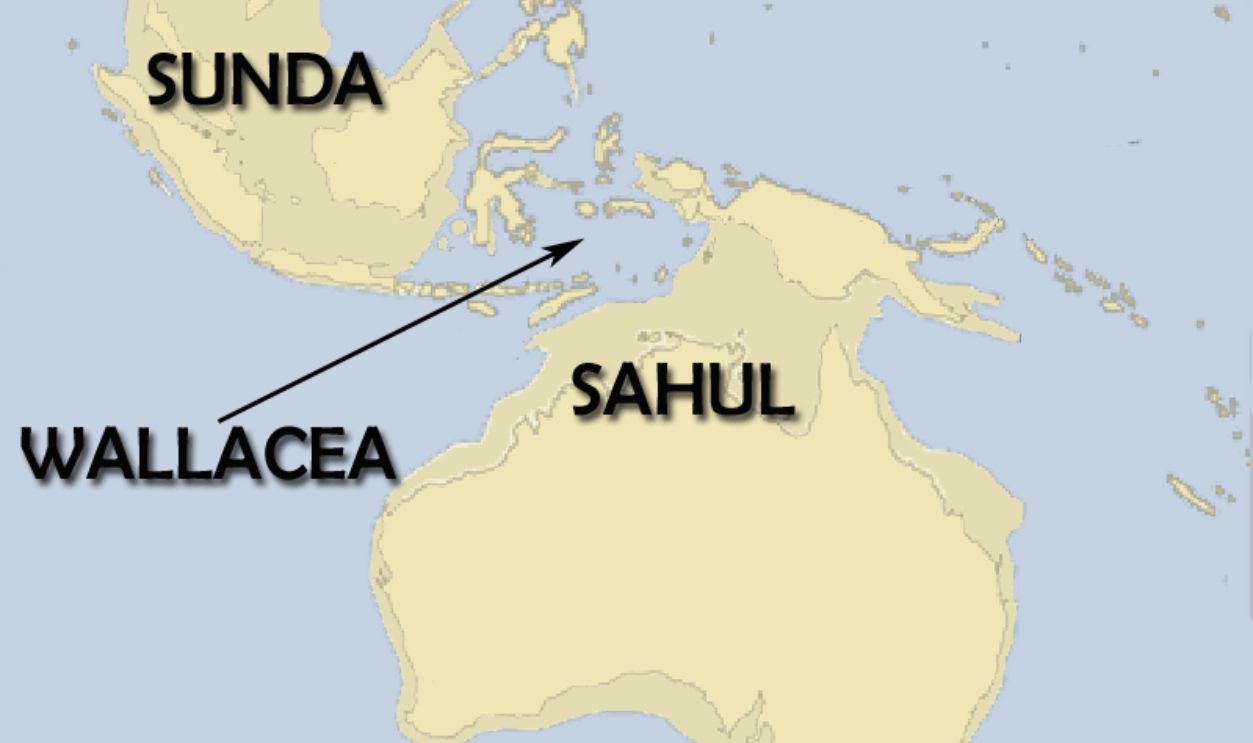
The Continents That Shaped Asian And Australian Species
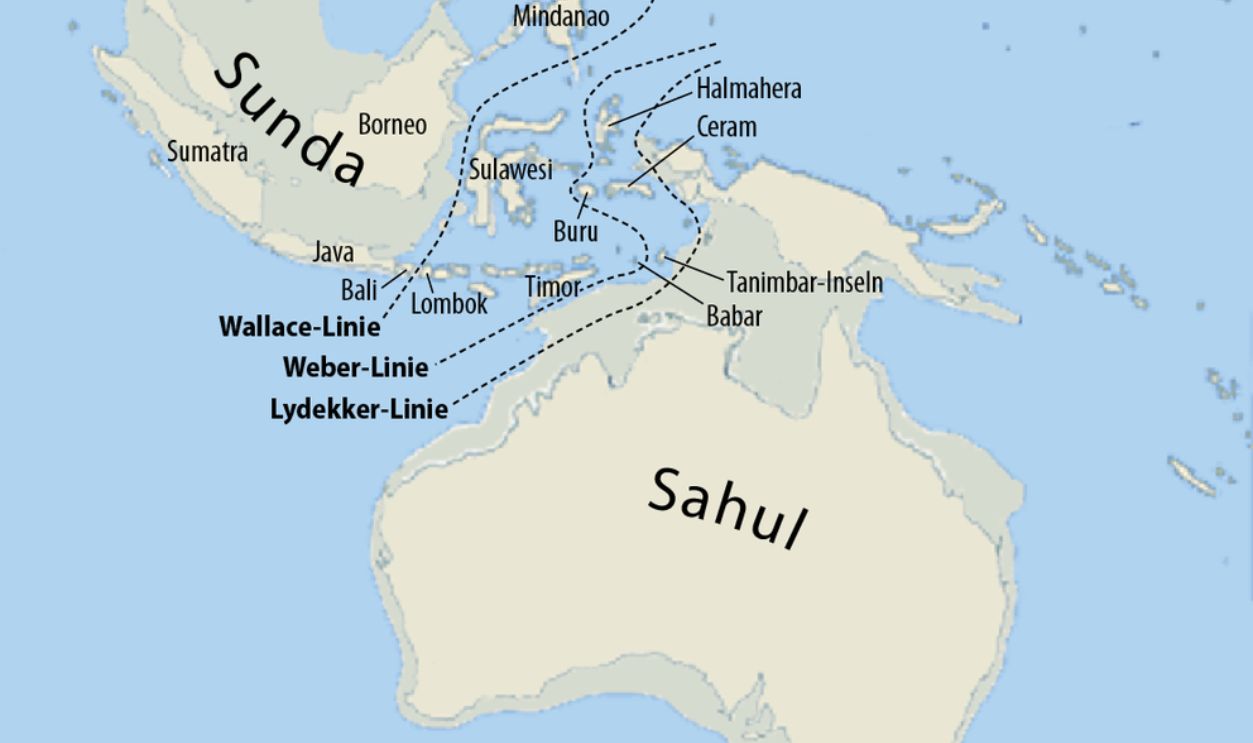
The Sunda and Sahul shelves are submerged continental areas underlying Southeast Asia and northern Australia. These shelves reveal ancient connections—Sunda once linked islands like Sumatra and Borneo to the Asian mainland, while Sahul connected New Guinea and Australia.
 Christophe cagé, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Christophe cagé, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Distinct Flora And Fauna
Species from each shelf evolved to adapt to their respective regions, creating the biodiversity divide. The differing climates and physical separation on these shelves reinforced the distinct flora and fauna between these two regions, a pattern seen in their separated ecosystems today.
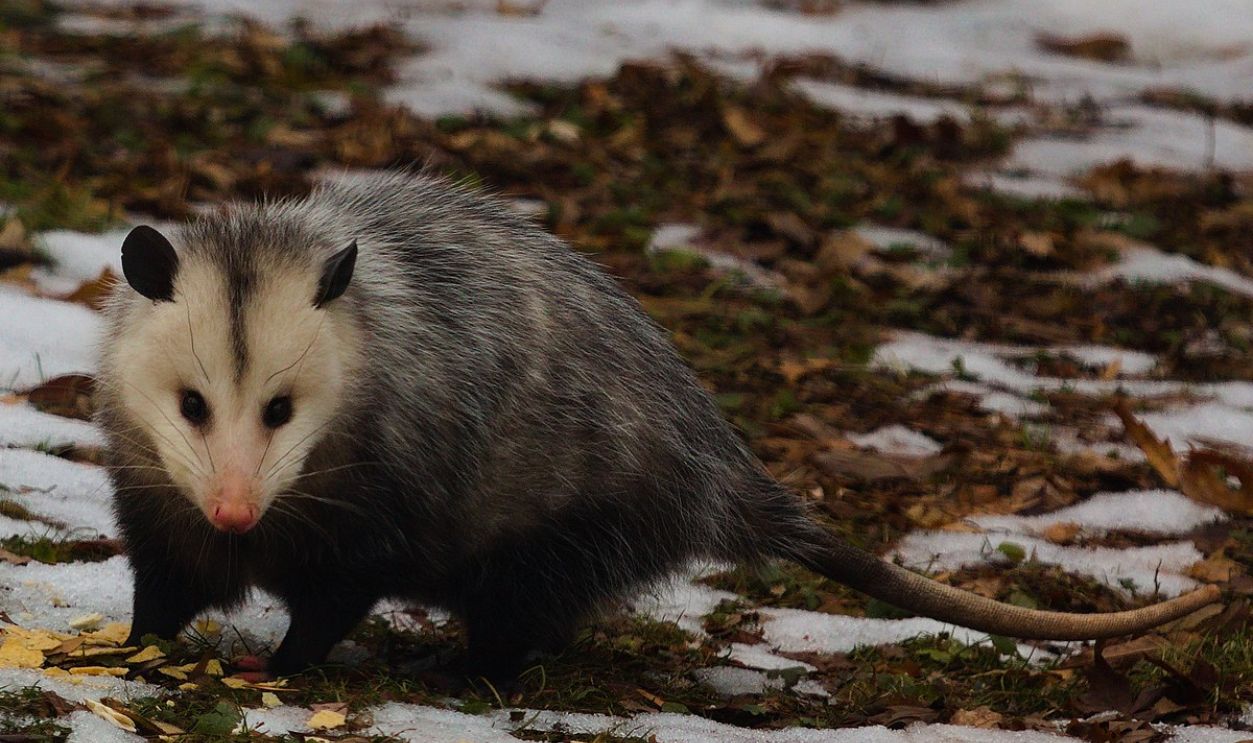 Mathieu Landretti, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Mathieu Landretti, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Sea Level Changes Contributed To The Wallace Line's Formation
During ice ages, lower sea levels exposed land bridges in the region, enabling some species to cross areas that are now submerged. However, even at these times, deeper straits like the Lombok and Makassar prevented complete intermingling.
 Ice Age Centre, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Ice Age Centre, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Deeper Channels Preserved The Wallace Line
These waters have historically acted as barriers, keeping many Asian and Australian species apart. With rising and falling sea levels, land connections fluctuated, but the deeper channels consistently preserved the Wallace Line as a natural boundary, illustrating how sea level changes influenced species distribution.
 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Black_Sea,_Fiolent,_Crimea.jpg
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Black_Sea,_Fiolent,_Crimea.jpg
The Role Of Ice Ages In Southeast Asia's Biodiversity
Ice ages were game-changing in Southeast Asia's biodiversity by lowering sea levels and allowing limited species migration across land bridges. However, the depth of waters between islands in the region, particularly around the Wallace Line, created enduring divides even when the seas receded.
Glacial Periods
This isolation during glacial periods helped prevent extensive species mixing, fostering the biodiversity observed today. The repeated fluctuation of sea levels during glacial cycles helped maintain these unique ecosystems, contributing to the genetic and ecological diversity seen across the Malay Archipelago.
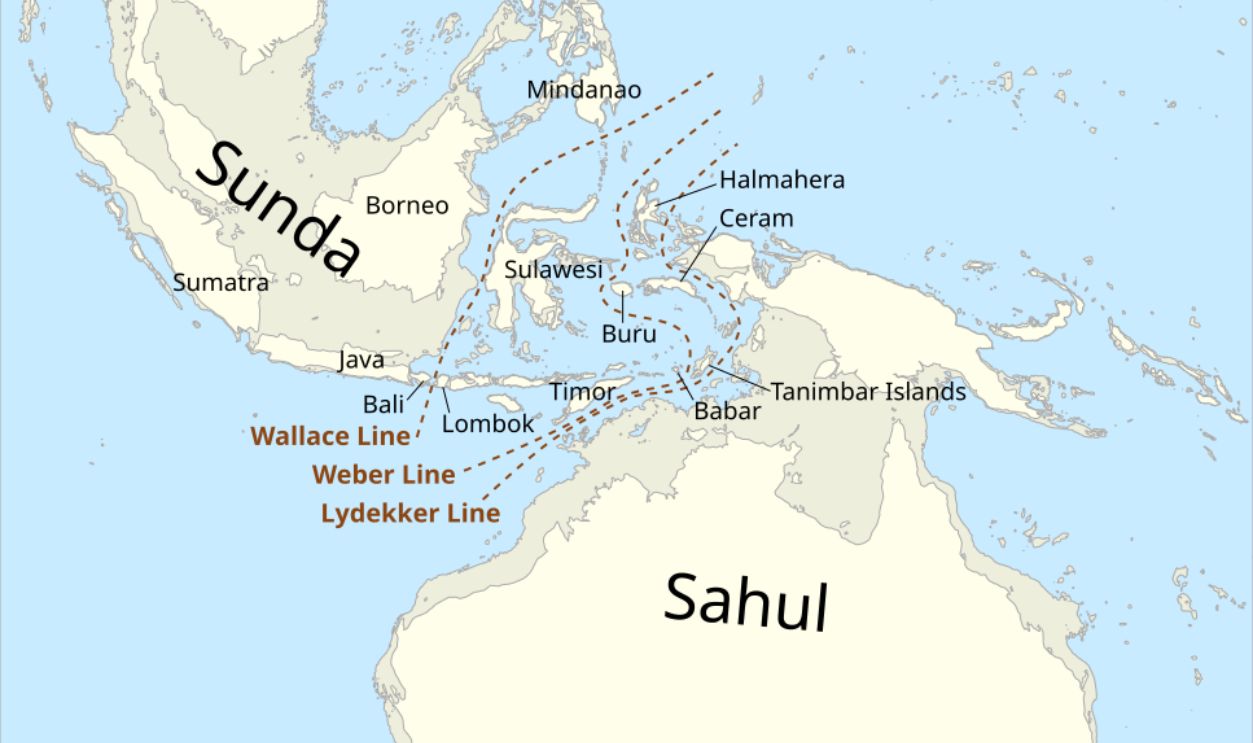
Wallacea Was Formed By Shifting Tectonic Plates
The Wallacea region, located between the Wallace and Lydekker lines, is an area where Australian and Asian faunas blend. Unlike the more stable Sunda and Sahul shelves, Wallacea comprises numerous islands formed from tectonic activity, creating isolated habitats for species.
 Muriel Gottrops, Wikimedia Commons
Muriel Gottrops, Wikimedia Commons
A Mix Of Influences
This region, named in honor of Wallace, harbors unique species that reflect a mix of influences from both realms. Wallacea acts as a transition zone, offering scientists insight into the biogeographical influences that shaped species distribution and adaptation across Asia and Australia.
 Maximilian Dörrbecker (Chumwa), CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Maximilian Dörrbecker (Chumwa), CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
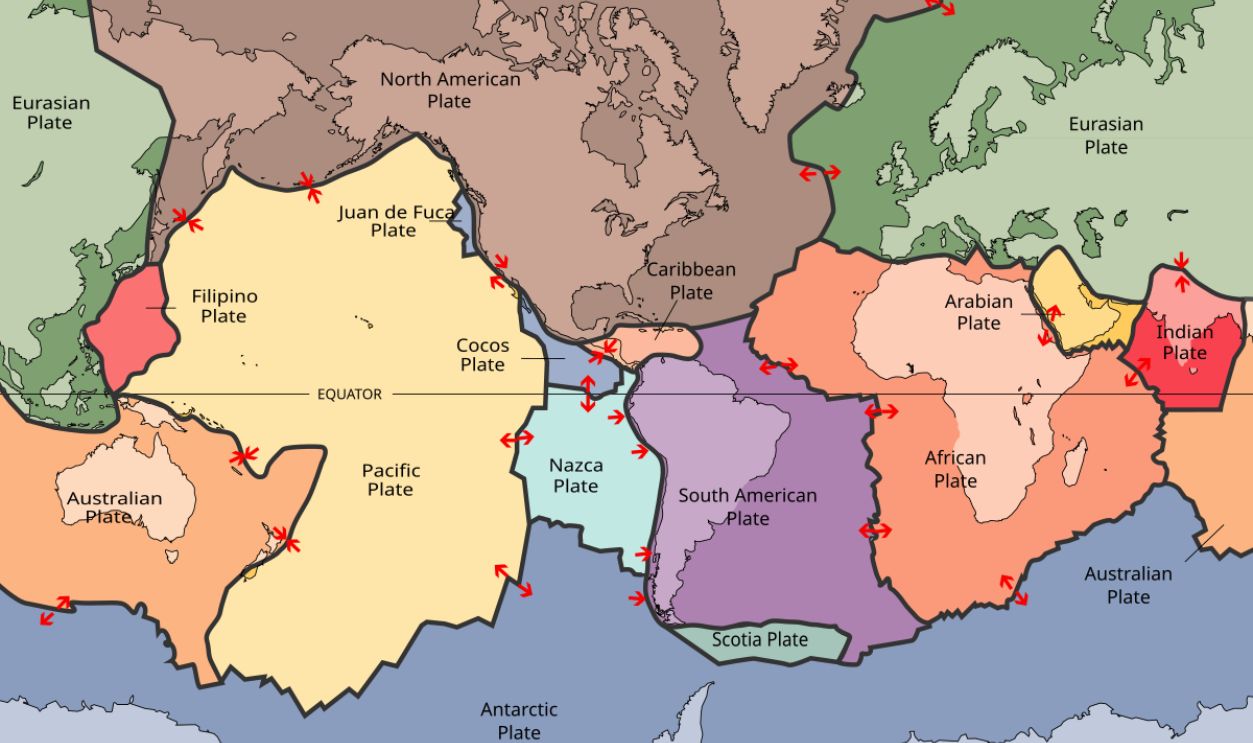
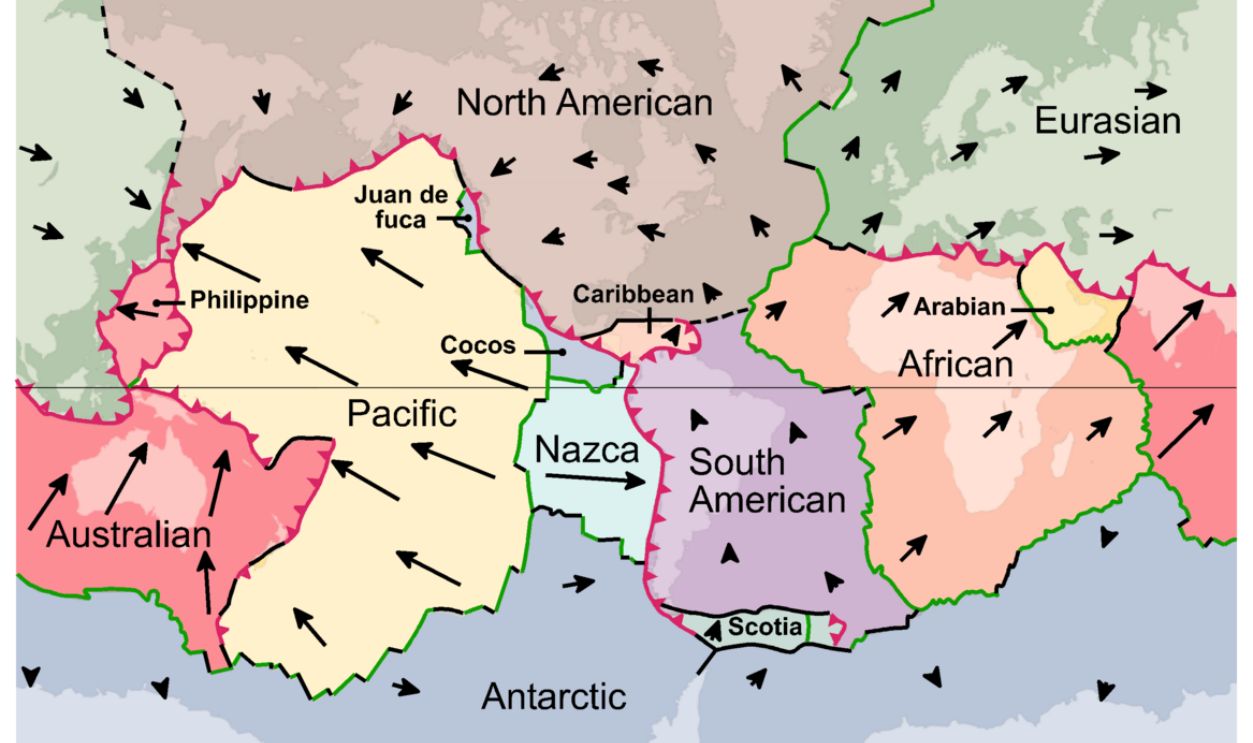
Understanding Indonesia's Complex Tectonic Plates
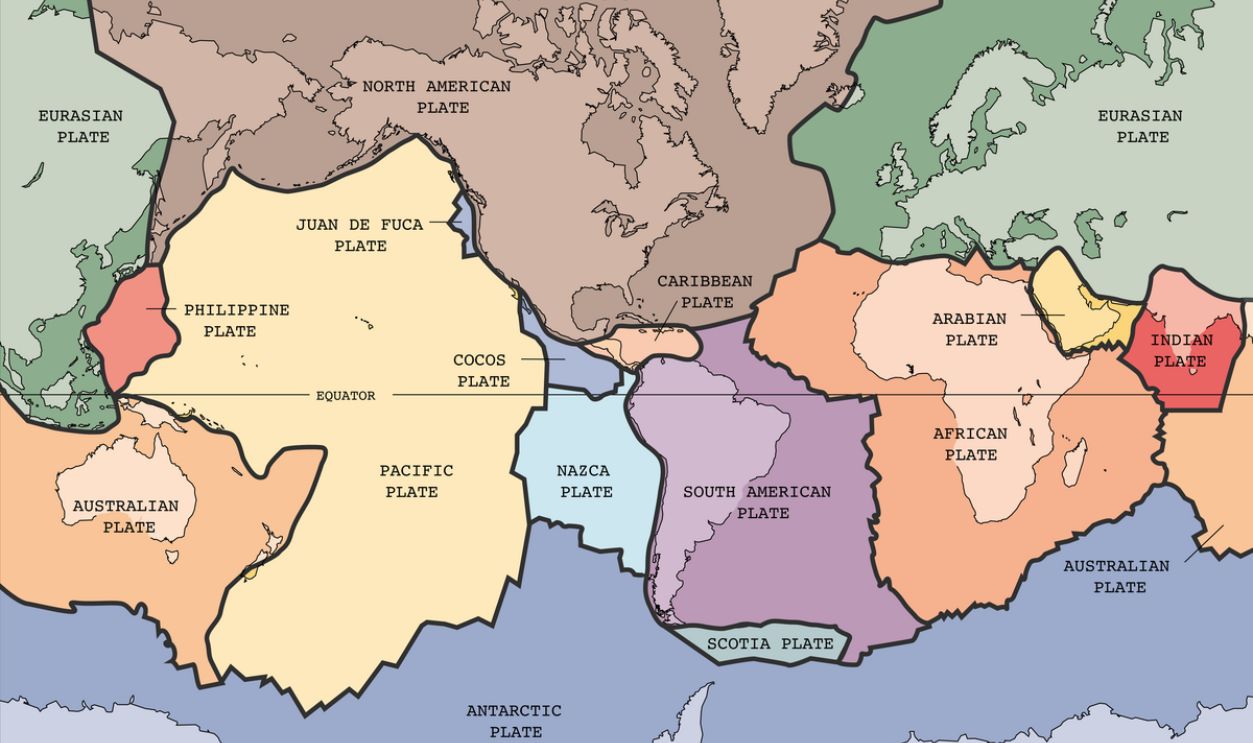
Indonesia sits atop several tectonic plates, including the Eurasian, Indo-Australian, and Pacific plates, which collide and create one of the world's most tectonically active zones. This movement results in frequent volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, contributing to the region's complex geography and unique habitats.
Creation Of Isolated Environments
The Wallace Line's placement aligns with these tectonic divides, as volcanic islands like those in Wallacea arose from tectonic activity. This geological complexity has created isolated environments that house diverse species, showcasing how Indonesia's geological features contribute to its rich biodiversity.
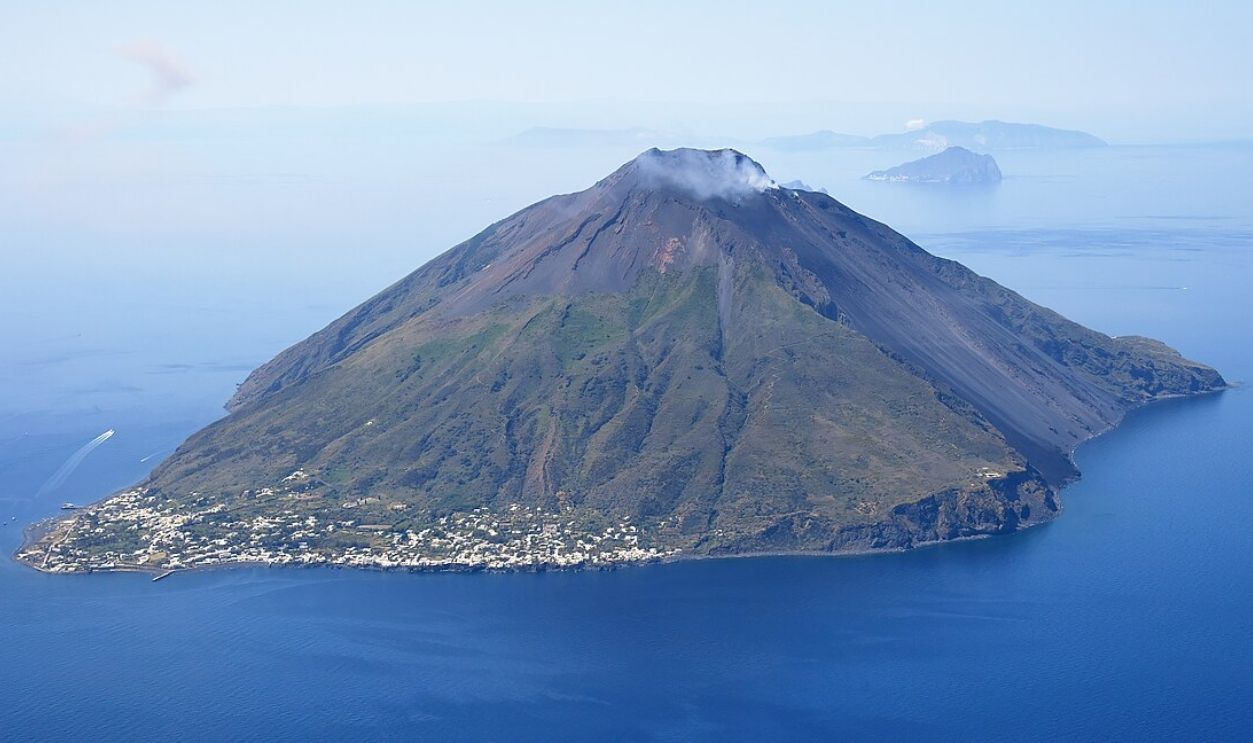 Carsten Steger, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Carsten Steger, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Influence Of Asia And Australia's Distinct Continental Shelves
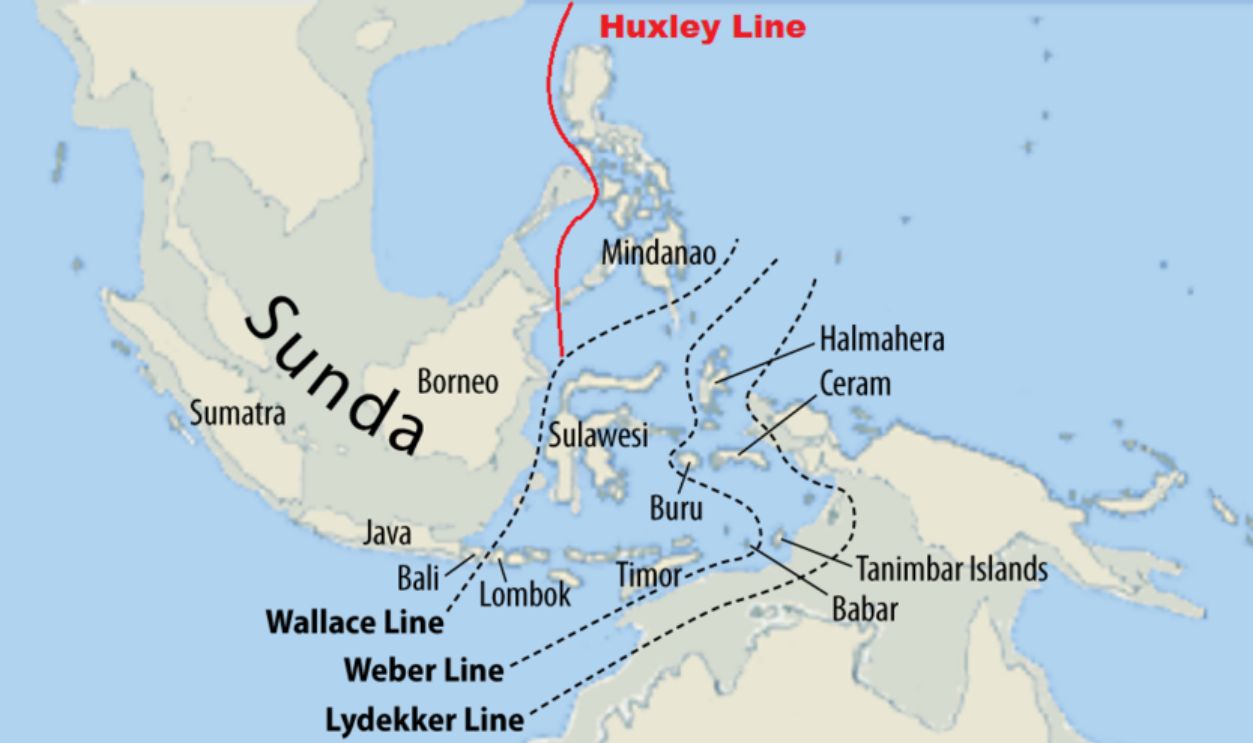
The Wallace Line corresponds closely to the boundaries between the Sunda and Sahul continental shelves. These underwater landmasses, which include much of Asia and Australia, played a critical role in shaping the line. Without the needed tools, Wallace was able to identify the borders between them.
 Altaileopard, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Altaileopard, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
A Natural Separation
When sea levels were low during the ice ages, land bridges formed, allowing limited species migration across the region. However, deep trenches between these shelves prevented complete mixing, helping maintain distinct ecological identities on either side. This geological feature created a natural separation.
The Evolutionary History Of The Komodo Dragon
The Komodo dragon, a unique inhabitant of Wallacea, reflects the line's evolutionary influences. Fossil evidence shows that this large monitor lizard originated in Australia before dispersing to Wallacean islands around a million years ago. The Wallace Line kept its range limited to certain islands, preventing it from migrating westward.
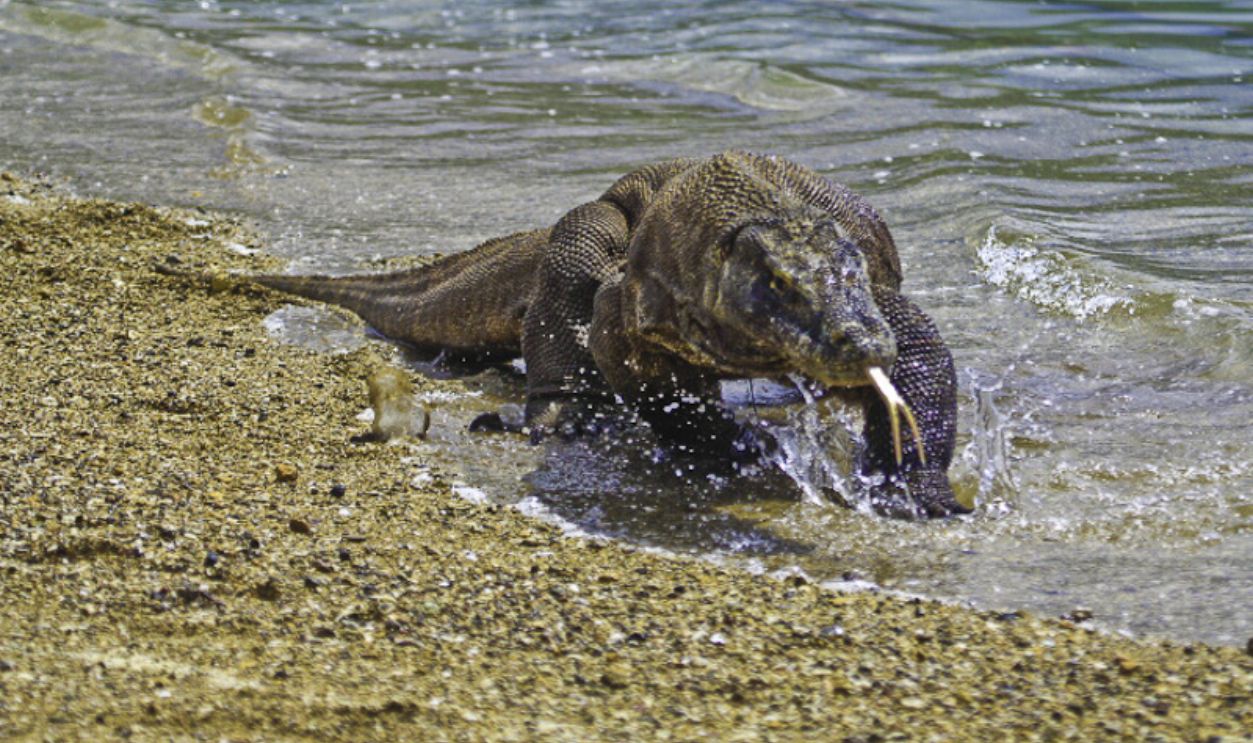 Adhi Rachdian, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Adhi Rachdian, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
A Prime Example
The Komodo dragon is a living example of how physical and environmental barriers shaped species' evolutionary paths. It remains confined to its eastern habitat within the Wallacea region, unable to go back to Australia or move to Asia.
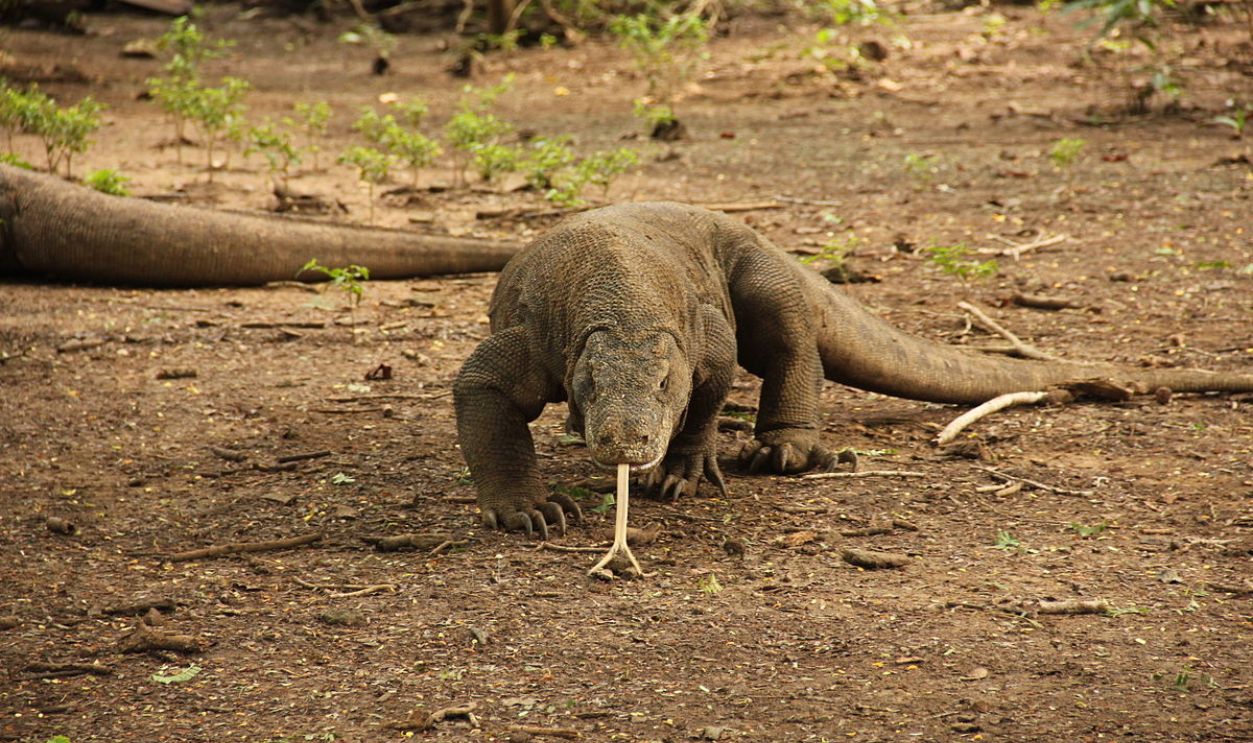 Viglianti, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Viglianti, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Do Birds And Insects Respect The Wallace Line?
Birds and insects, despite their mobility, often observe the Wallace Line as a boundary. This pattern reflects the ecological conditions and selective pressures on either side of the line, where many species are finely adapted to specific habitats.
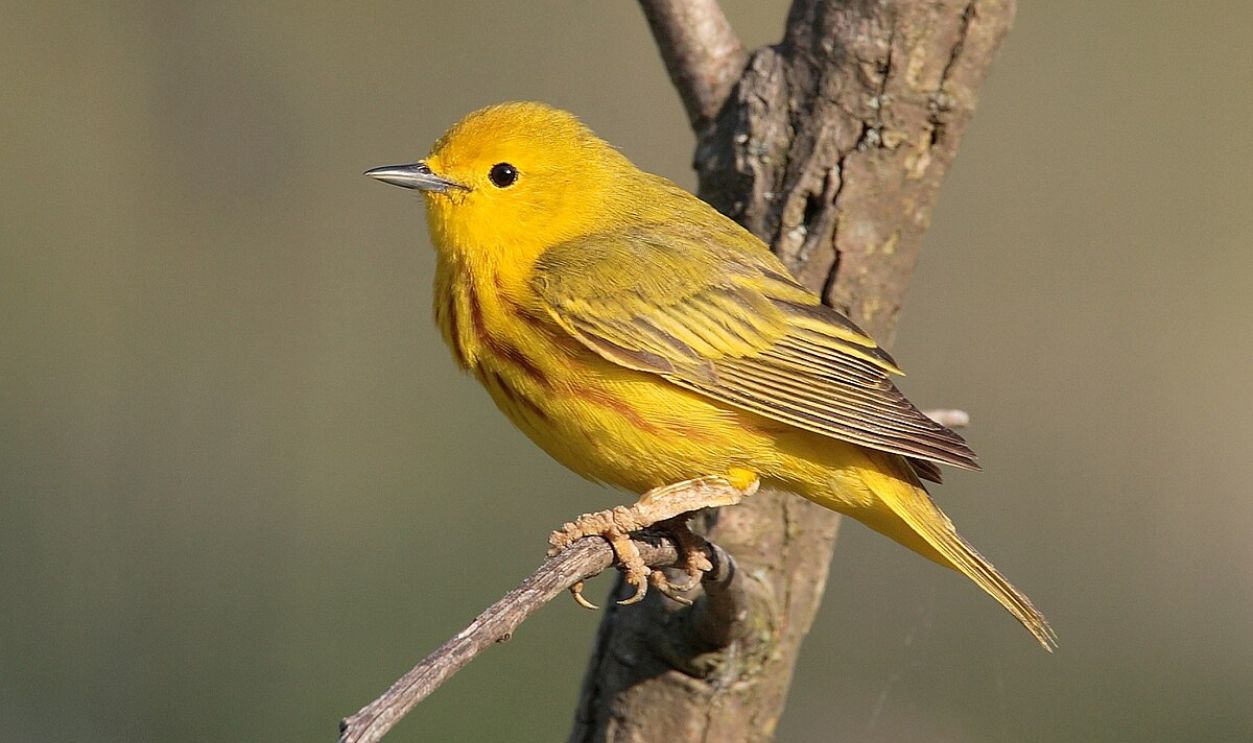 Mdf, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Mdf, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Strong Currents Between Islands
Additionally, the strong currents between islands make it challenging for even flying species to traverse. Birds and insects tend to adapt to the conditions on their side of the line, reinforcing the stark biodiversity boundary identified by Wallace, even among species with the capability to fly across the water.
 Alan D. Wilson, CC BY-SA 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
Alan D. Wilson, CC BY-SA 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
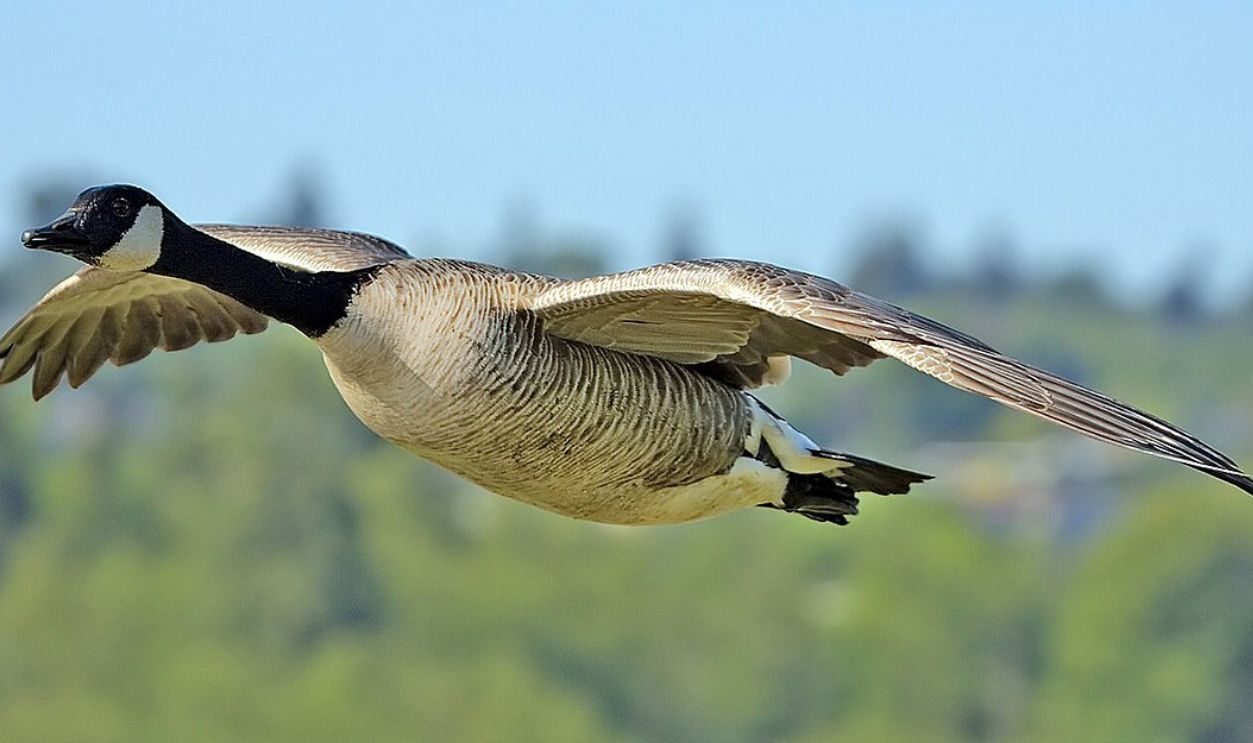
Wallace's Observations Of Bird Species
Birds played an important role in Wallace's discovery. While studying the islands of Bali and Lombok, he observed that certain bird species were exclusive to each side. For instance, Java and Bali hosted the yellow-headed weaver and coppersmith barbet, while they were absent from Lombok, which featured entirely different birdlife.
 Dominic Sherony, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Dominic Sherony, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
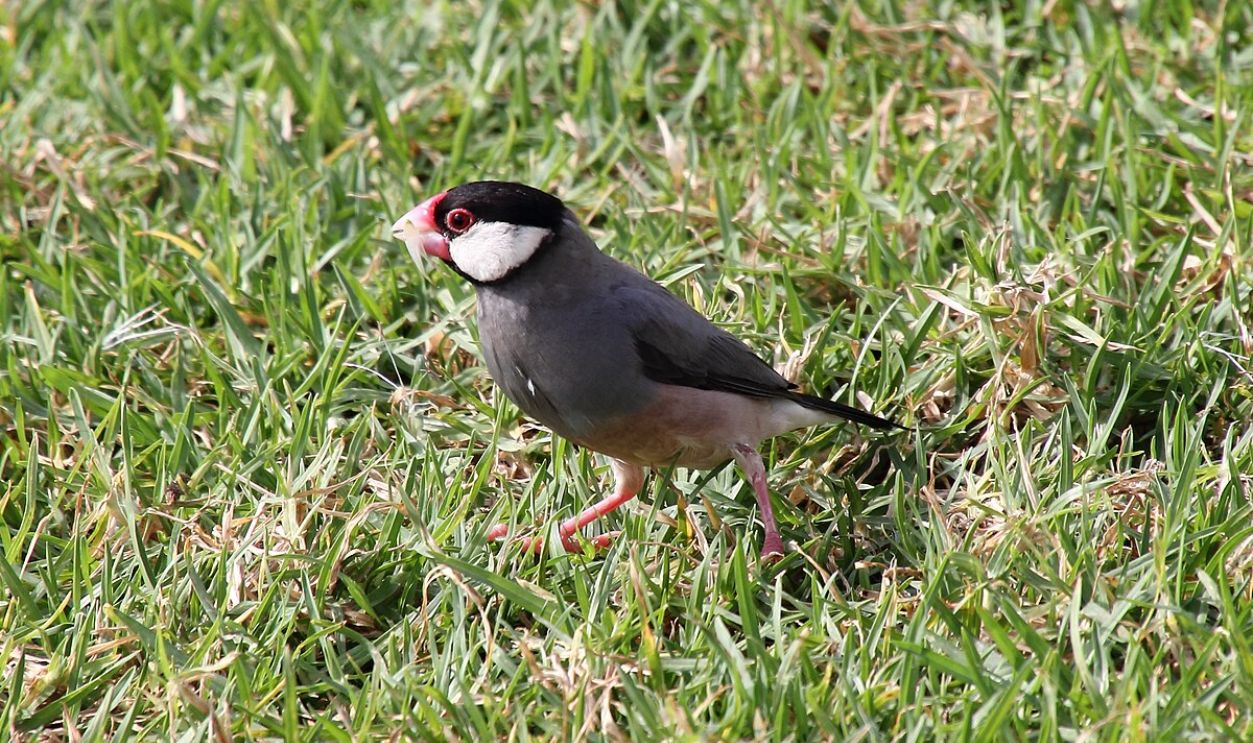
Findings On Bird Biodiversity
This sharp contrast, noted even among flying animals, supported Wallace's idea that geographic barriers influence species distribution. His findings on bird biodiversity significantly contributed to biogeography by showing how isolation could shape species composition.
 Mildeep, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Mildeep, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Different From Darwin
Wallace's insights into species distribution were revolutionary for his era, as he proposed natural selection and geographic isolation before plate tectonics was understood. Unlike Darwin's focus on adaptation, Wallace highlighted how geographic separations influenced where species evolved and survived.
 NicholasToal, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
NicholasToal, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Why Wallace's Theories Were Ahead Of Their Time
His observations introduced groundbreaking ideas about evolution and laid the groundwork for biogeography, a field that emerged in full recognition only decades later. Wallace's theories continue to inform ecological research as scientists explore how geographic and environmental barriers impact biodiversity globally.
 Marchant, James, Wikimedia Commons
Marchant, James, Wikimedia Commons
Wallace's Research Inspired Modern Biogeography
Wallace's studies were pioneering in the development of biogeography, inspiring a scientific approach to understanding the distribution of life. His work helped establish biogeography as a discipline, influencing theories on speciation, migration, and biodiversity at a time when these concepts were considered novel.
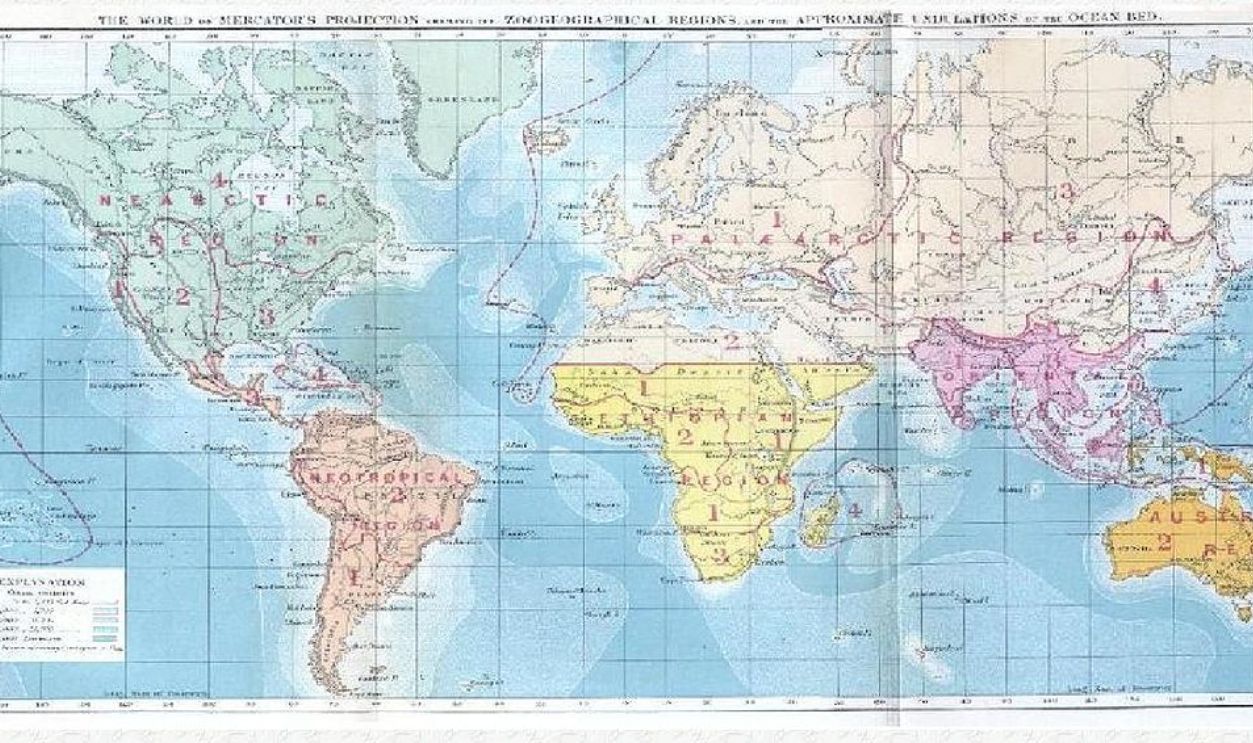 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Advanced Studies
Modern scientists continue to explore his concepts, using advanced techniques like genetic mapping and GIS tools to study species distribution. Wallace's legacy endures in today's conservation efforts and evolutionary studies, highlighting the relevance of geographic boundaries in ecological research and biodiversity preservation.
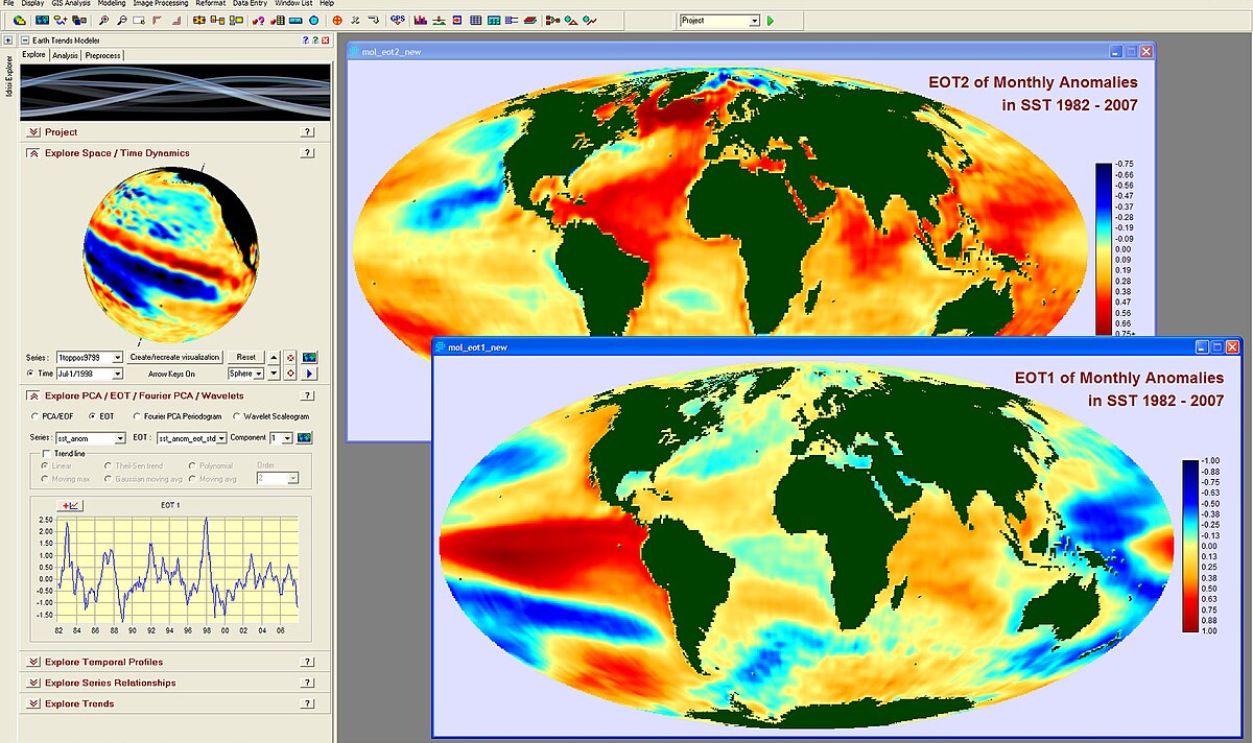 Clark Labs, CC BY 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Clark Labs, CC BY 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Modern Understanding Of Wallace's Findings On Plate Tectonics
Wallace's work predated the modern theory of plate tectonics, but his observations align well with current understanding. If Darwin takes the credit for telling us how different creatures came to be what they are, Wallace's theories explain how they got to be where they are.
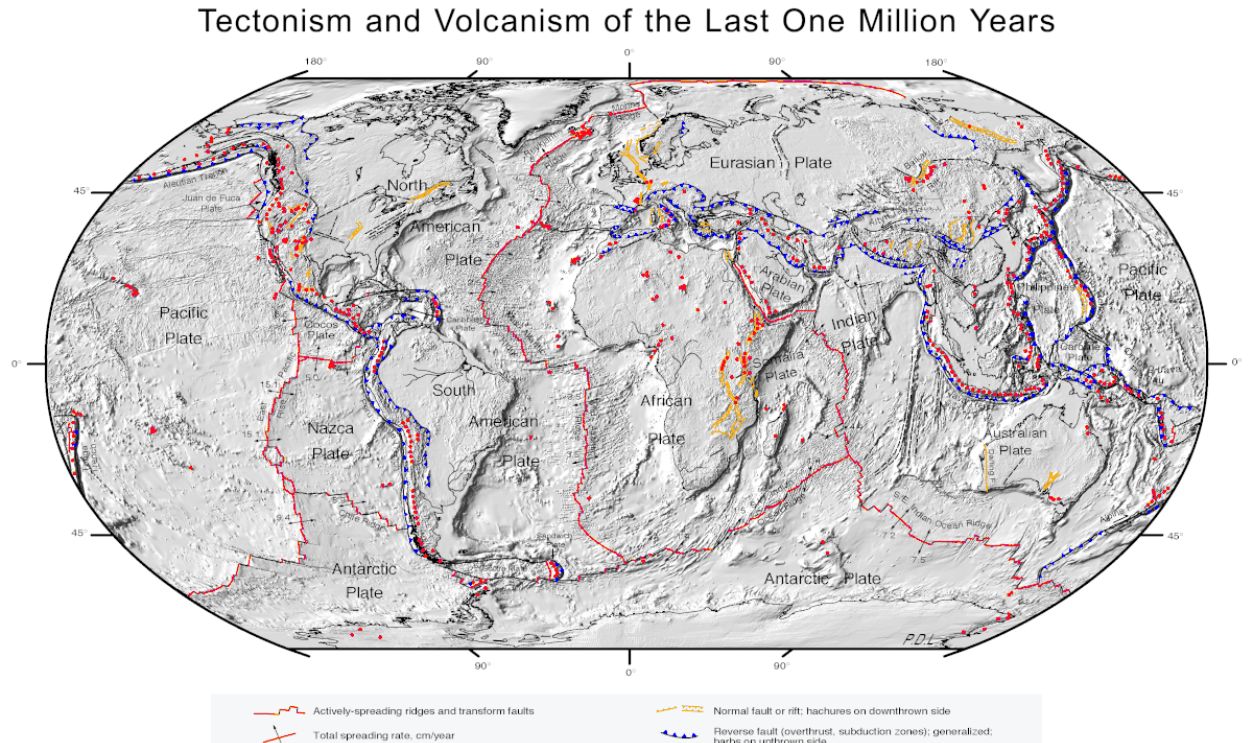 NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Wikimedia Commons
Advances In Plate Tectonics
The Wallace Line corresponds to tectonic boundaries between the Asian and Australian plates, supporting his observations of distinct ecosystems. Advances in plate tectonics have reinforced Wallace's legacy, demonstrating how geological forces shape ecological diversity across continents and contribute to the unique biogeographic divisions he described.
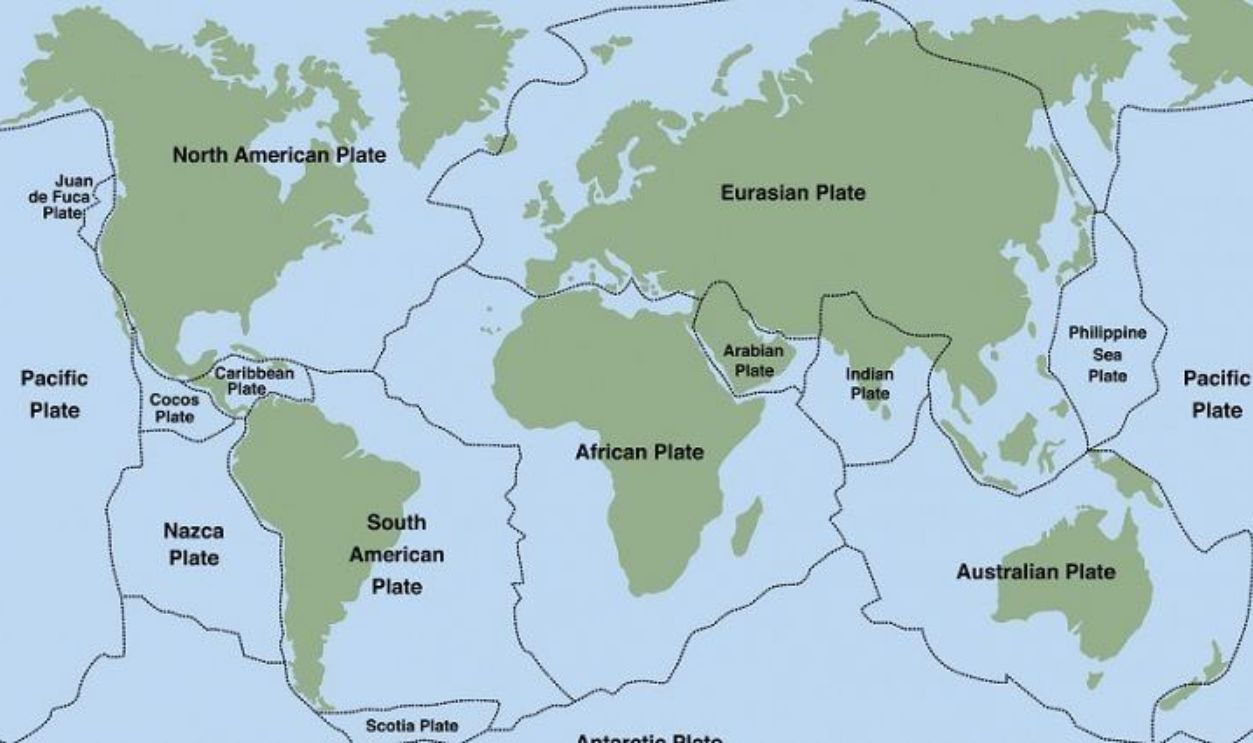 Fathimahazara, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Fathimahazara, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
How The Wallace Line Influences Conservation Efforts Today
Conservationists use the Wallace Line to prioritize biodiversity preservation in areas with high levels of endemism. As species on each side of the line evolved separately, they have distinct ecological roles that are threatened by climate change and subsequent habitat loss.
Preserving Unique Habitats Within Wallacea
Efforts often focus on preserving unique habitats within Wallacea, where many species are found nowhere else on Earth. By using the Wallace Line as a reference, conservationists work to maintain these biodiverse ecosystems, emphasizing the importance of protecting areas with evolutionary significance.