Secrets Of Earth's Past Revealed
A 16-million-year-old sequoia holds secrets of Earth's distant past. Discover how this ancient tree reveals our planet's history.

Exploring The Unanswered Questions Of Our Origins
Throughout our existence, one desire we continually seek to satisfy is the answer to "How things come to be?" To this day, humans remain fascinated by the concept of evolution. Though we have gotten answers, there are still too many yet to be answered.
A Glimpse Into Deep Time
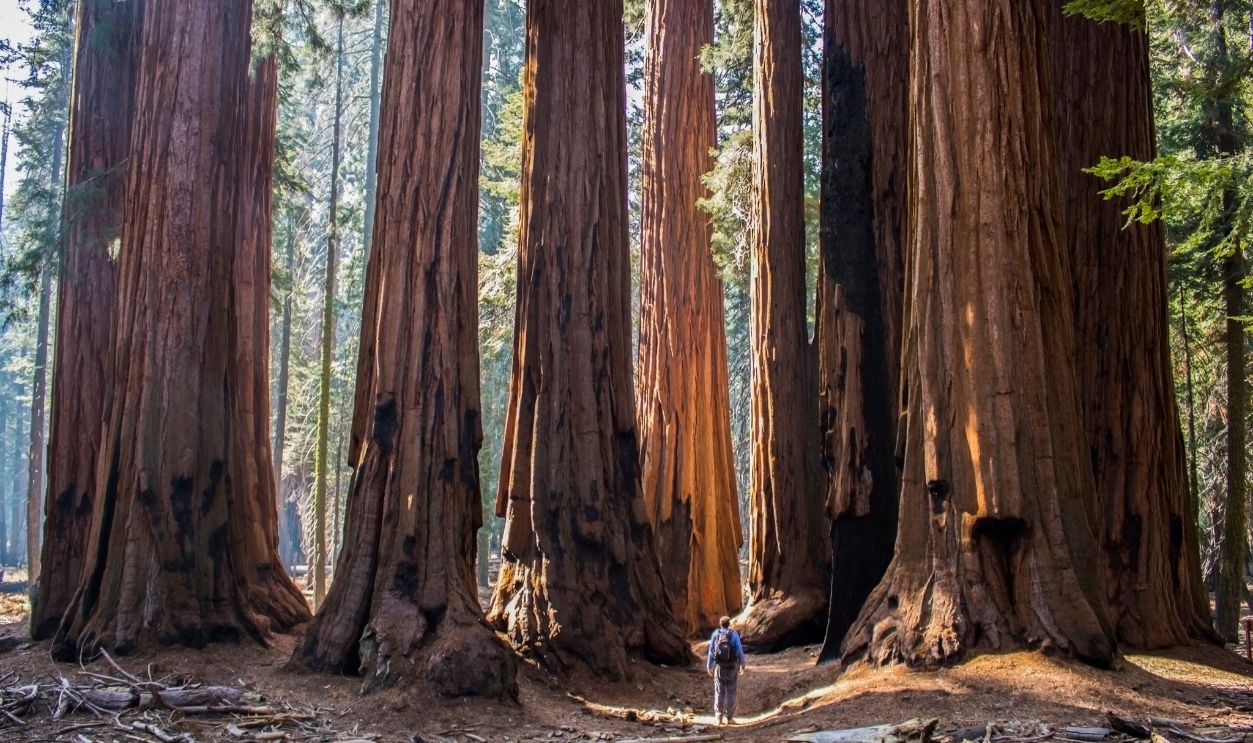
Looking into how ancient trees like the amazing 16-million-year-old sequoia came to be and dissecting every layer of it gives us an unusual knowledge of Earth's prehistoric timeline, which, in turn, will allow us to get a better understanding of our place in the natural world.
Sequoia (Suh-Kvoy-Uh)
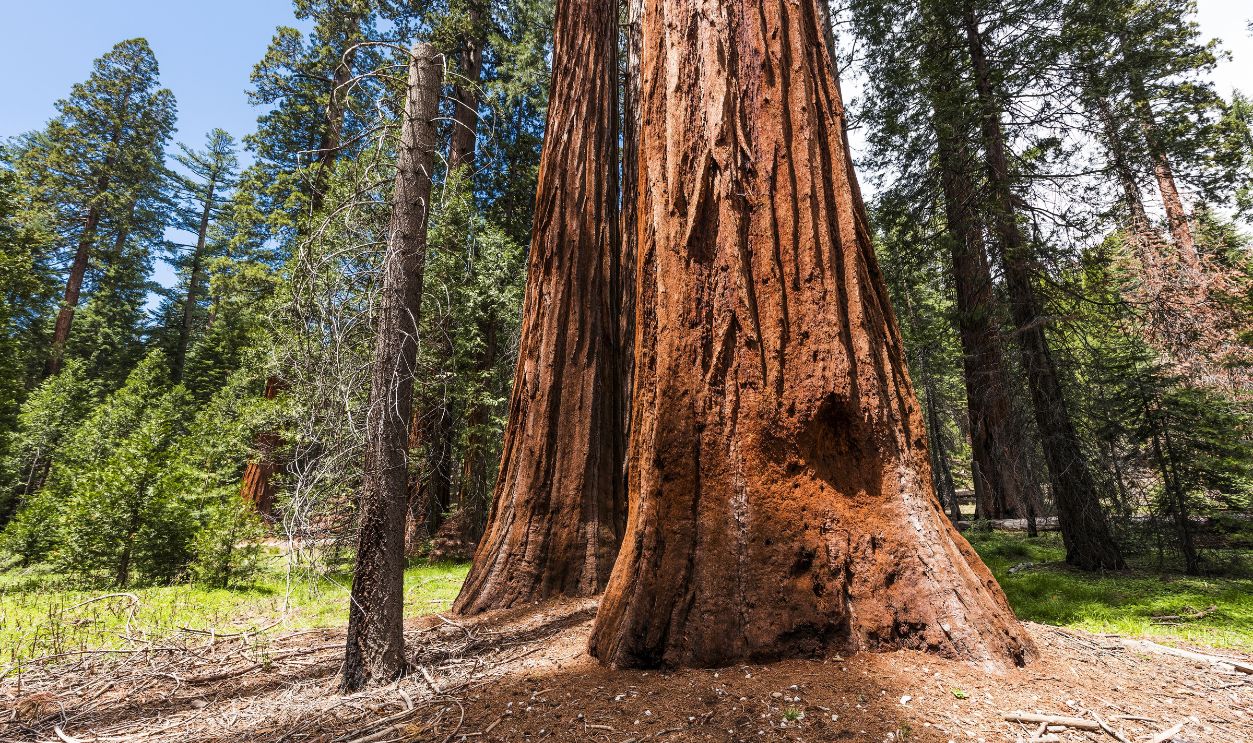
For clarity in this article, the word "sequoia" means an ancient species of massive tree that is specific to the conifer type and known for its size, longevity, and resilience. Sequoias also include some of the oldest and largest trees on Earth.
Seeking Answers From The Past
In the journey of seeking answers, we have assembled pieces of fossils, ruins, and artifacts to arrive at something. But understanding Earth's past requires much more than that; it requires special and unique relics, like ancient trees, that tell stories beyond human written records.
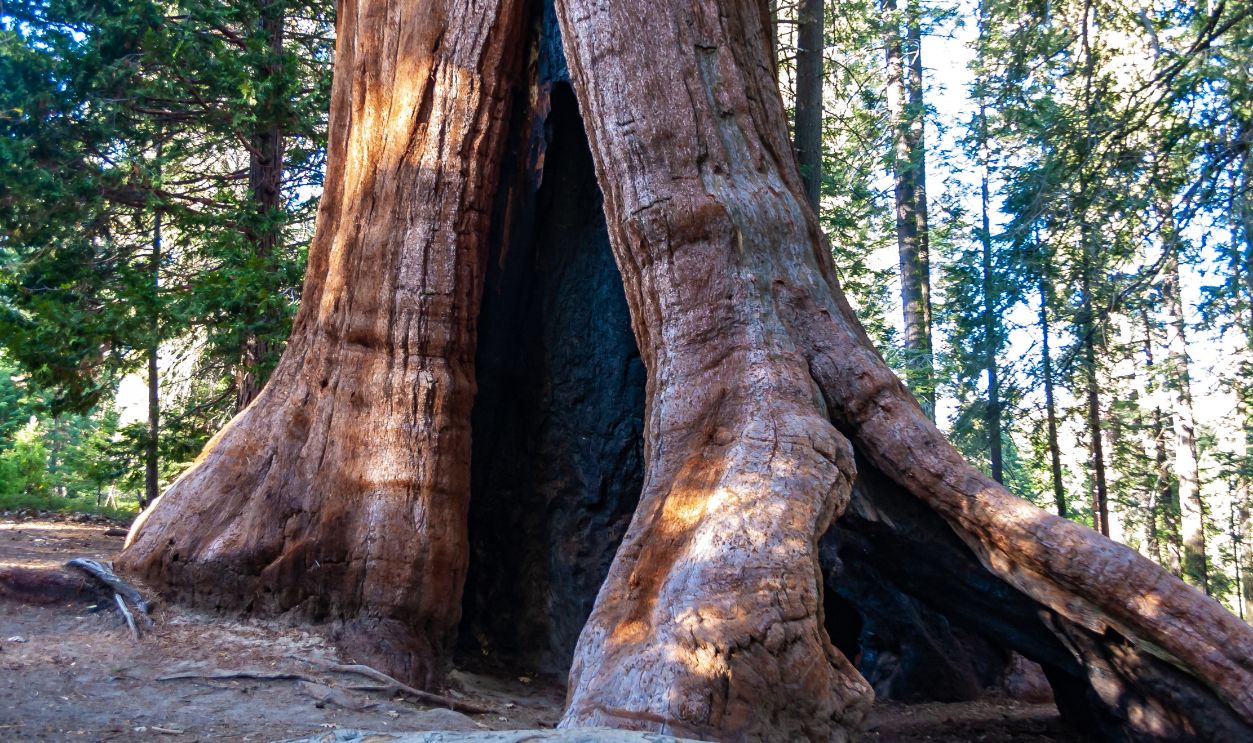
An Ancient Tree's Arrival At The Smithsonian
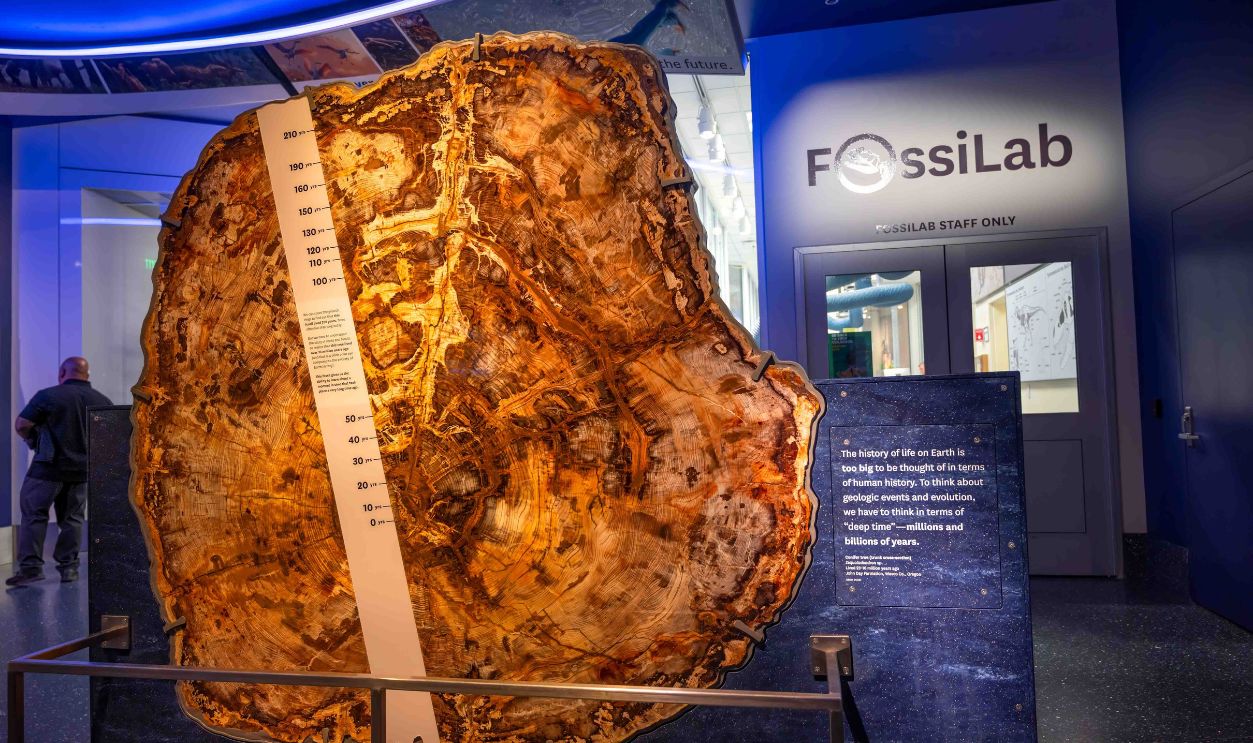
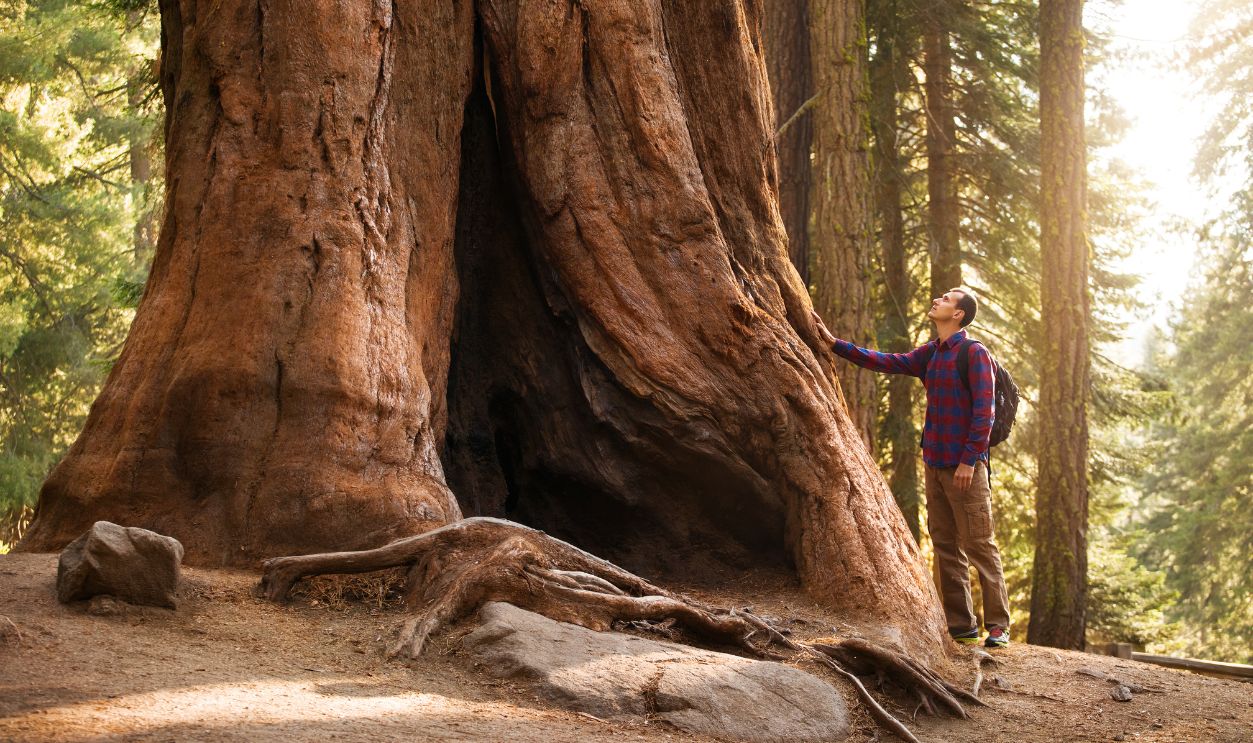
Something unimaginable arrives at the Smithsonian. Genuinely, not in our wildest imagination would we have thought that a preserved slab of a massive 16-million-year-old sequoia exists somewhere in central Oregon now, going back millions of years when the Earth was very different.
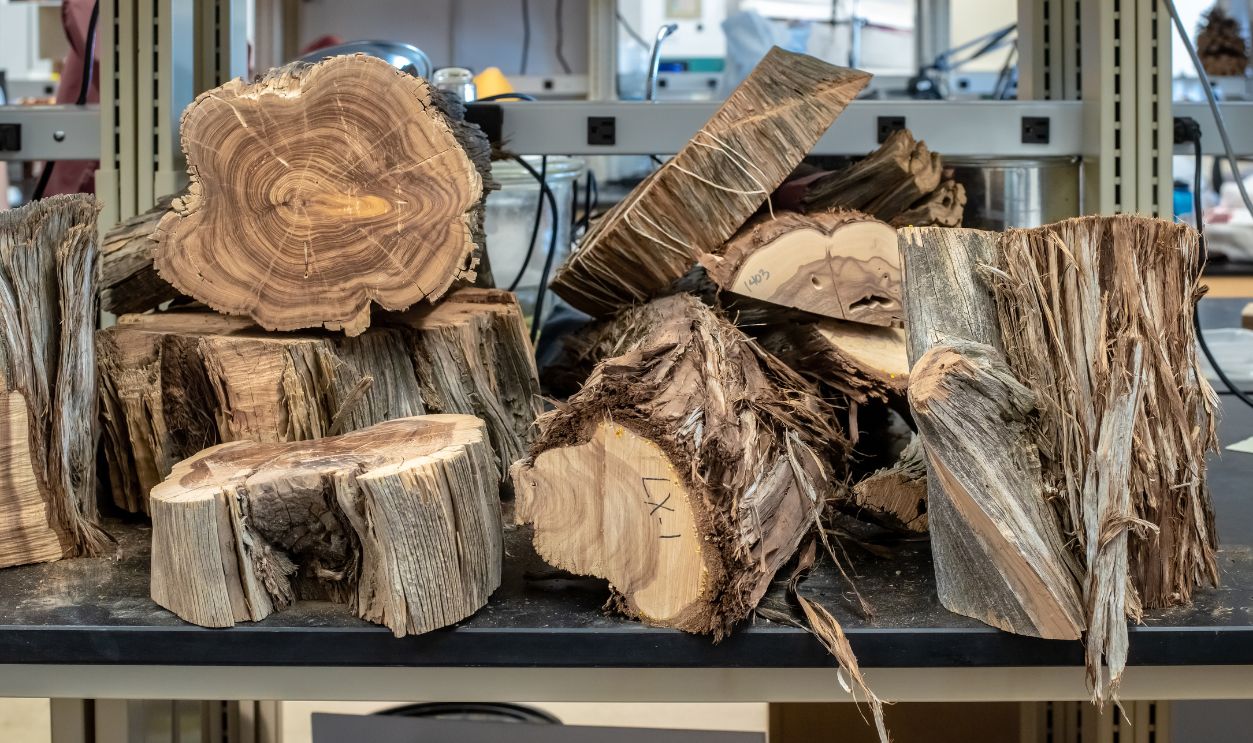
Scientist's Quest To Date The Tree
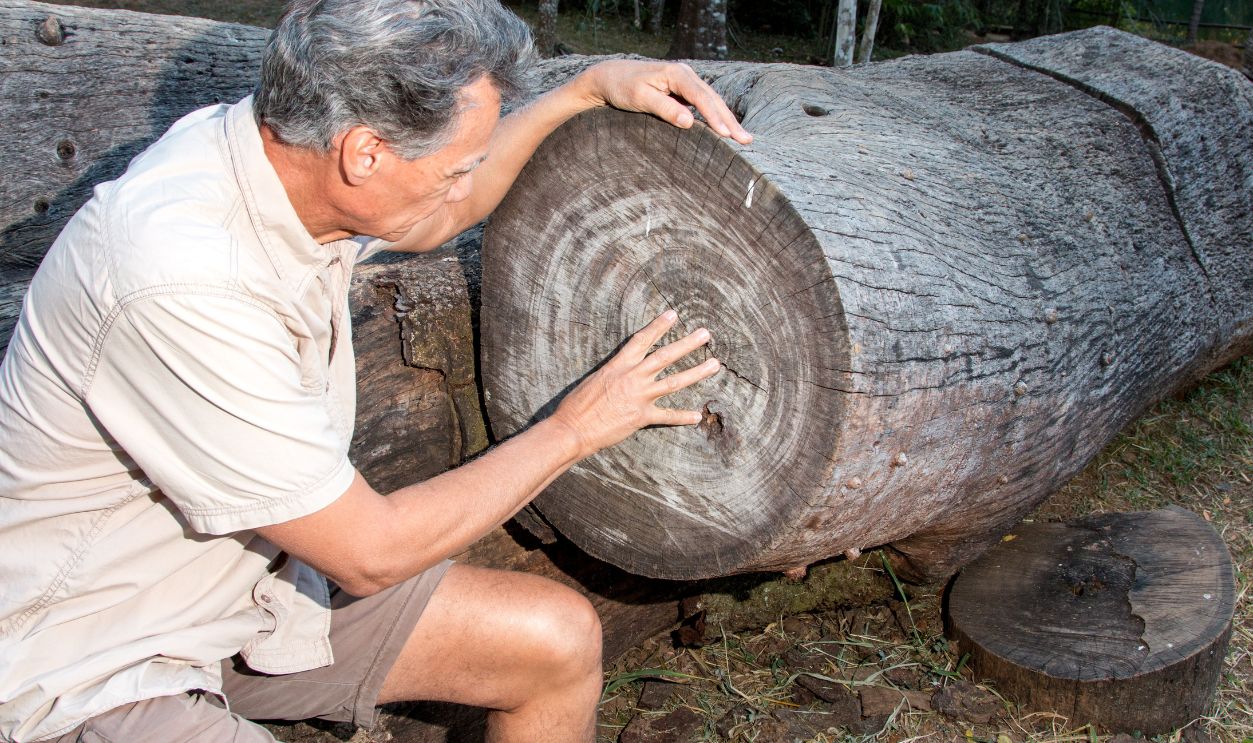
Paleobotanists have tirelessly counted the 260 rings to determine the tree's age. However, scientists have admitted that there might be a bit of an error and are open to correction, which is one of the beauties of scientific curiosity and the nature of discovery.
 Lucky-photographer, Shutterstock
Lucky-photographer, Shutterstock
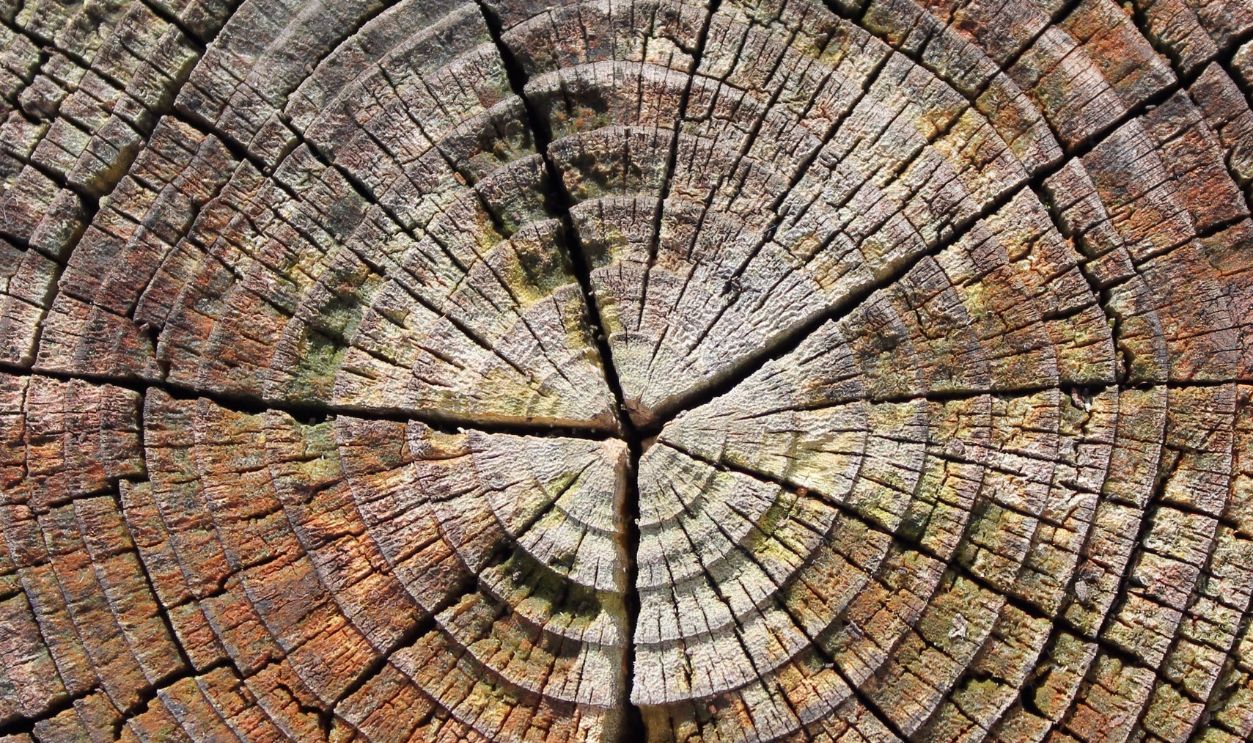
What Are Tree Rings?
Tree rings form every year, with each layer creating a mark that shows a season of growth. The thickness of each ring reveals changes in climate and environmental factors that might have affected or impacted the tree during that year.
The Science Of Tree Rings: Dendrochronology
Dendrochronology, the study of tree rings, gives researchers a deeper understanding of past climate and environmental conditions by examining patterns in every ring. Each one represents a year of growth, with its size, characteristics, and environmental changes contributing to our understanding of Earth’s history.
Trees As Ancient Climate Recorders
Trees that evolved around 380 million years ago keep their annual climate data within the rings. This means that each ring reflects a particular growing condition and gives clues about the temperature, rainfall, and atmospheric patterns each year. With this, scientists are able to piece together the planet's climate past.
Learning From Global Tree Records
One tree will not provide us with all the information we seek. To get the full picture, working with tree ring data from different global sites will provide a rich climate chronology. By combining thousands of tree rings, scientists are able to see patterns in past climate events and shifts.
 Dominic Gentilcore PhD, Shutterstock
Dominic Gentilcore PhD, Shutterstock
Guiding The Future Through Past Climate Insights
Another way to guide the future through its past is to analyze ancient tree growth patterns. This will help decipher how past climate changes impact ecosystems. With this understanding, scientists are able to predict how future changes may affect trees and other life forms.
What Tree Rings Reveal About Climate
By properly and carefully analyzing ring patterns, scientists can determine climate conditions over centuries, thereby understanding how trees and their ecosystems respond to changes. This is a very important tool for studying climate history and its future impacts.
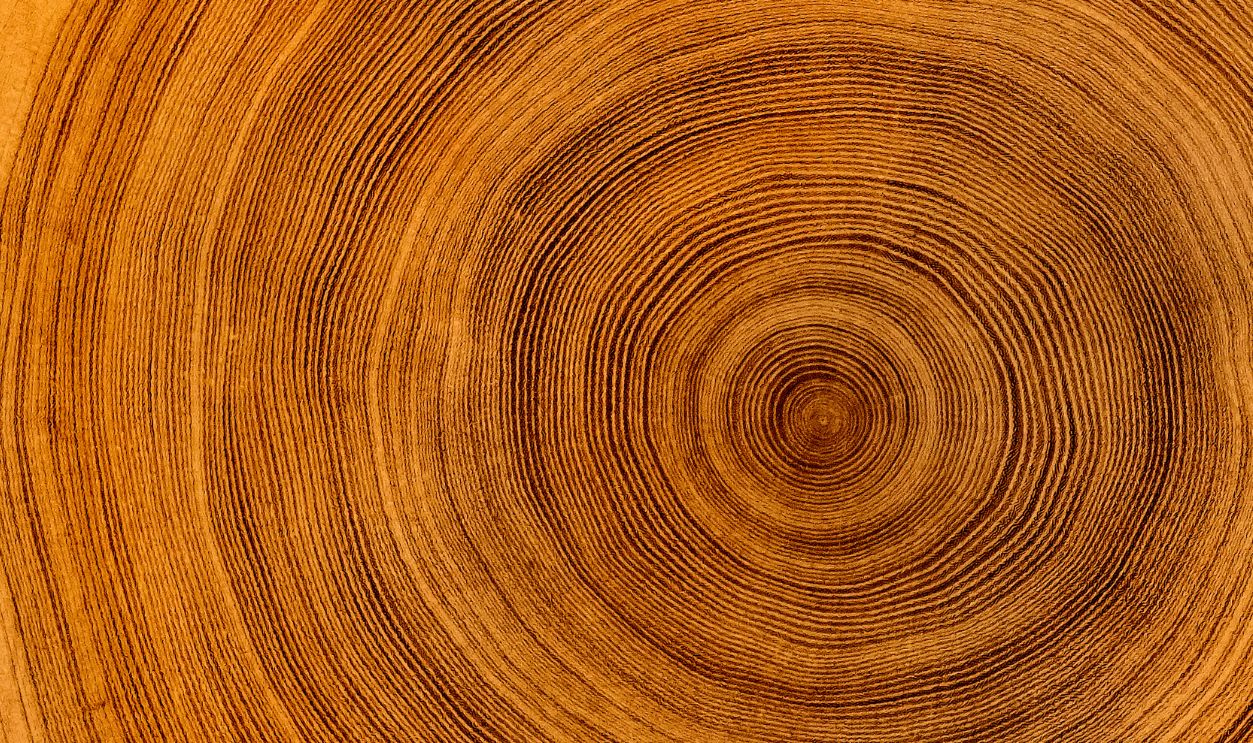
The Sequoia's Life In 260 Rings
This sequoia's 260 rings indicate an era of thriving growth followed by a slower, gradual aging process. It is worth noting that the early rings reveal rapid growth, while the later ones suggest a natural slowing of its life cycle as it matures.
 captureandcompose, Shutterstock
captureandcompose, Shutterstock
Rapid Growth In Youth, Slower With Age
From the close study, it was revealed that there was a pattern of rapid growth in its early years, which was almost followed by a slowdown. At first, the ring will be spaced widely, which shows fast growth, and then it will become narrow over time as the tree gets old and expands.
A Time Capsule Of Ancient Atmosphere
When the tree is alive, it takes CO₂ from the atmosphere and converts it to sugar and lignans; the reason is to build its structure. With this, the carbon is preserved within the fossilized rings, which gives scientists access to atmospheric conditions from 16 million years ago.
 Oleg Kovtun Hydrobio, Shutterstock
Oleg Kovtun Hydrobio, Shutterstock
Silica's Role In Preservation
After the tree died, the water that contained minerals, mostly silica, slowly covered its cells. With time, the silica changes the tree into a "glass-like" fossil for two reasons: one is to lock its ancient compounds, and the other reason is to protect its environmental history of millions of years.
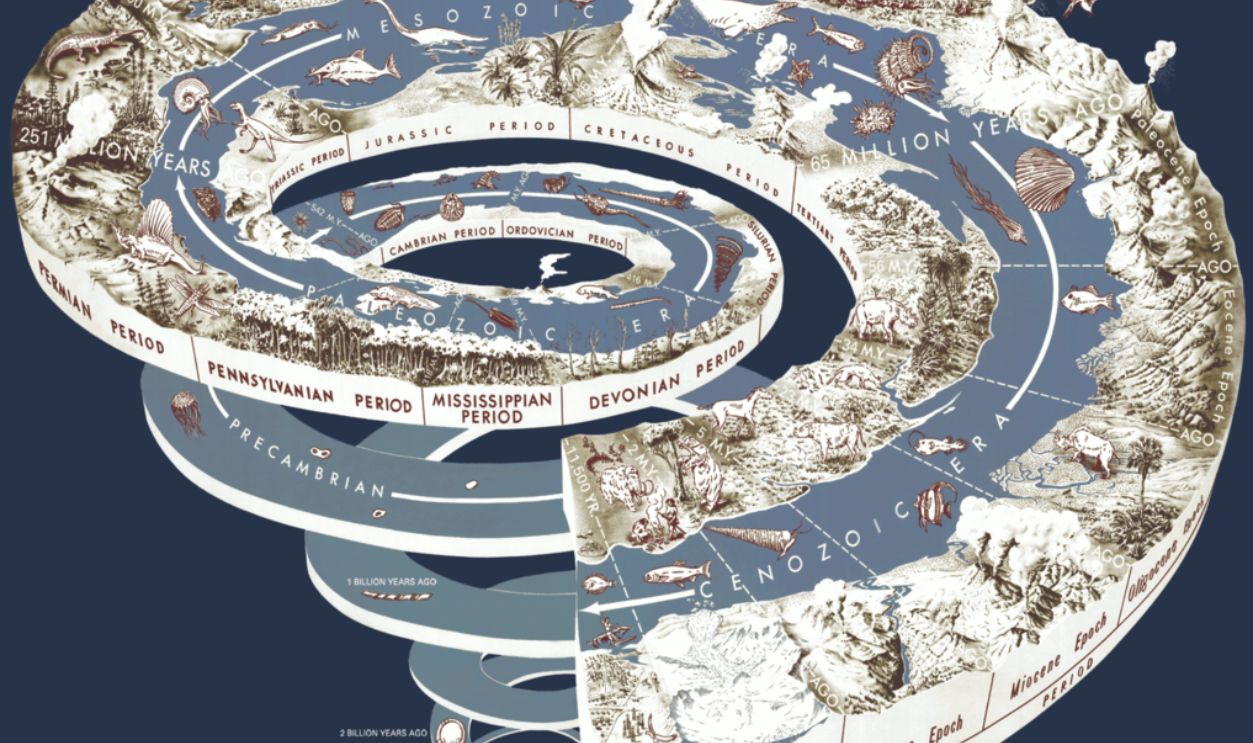
What Is Deep Time?
To understand where we are coming from, we have to trace our steps back to how we got here. The only way we can achieve this is through Deep Time, a massive stretch of Earth's history, from when it was formed to the present day. Ancient trees give us a peek into this enormous timeline, linking us to life from billions of years ago.
 United States Geological Survey, Wikimedia Commons
United States Geological Survey, Wikimedia Commons
Understanding Our Place In Deep Time
In our interactions with the world since its discovery, humans only have a few thousand records of themselves and the world around them. Deep Time is much more than that. This sequoia urges viewers to imagine their place within a history dating back billions of years.
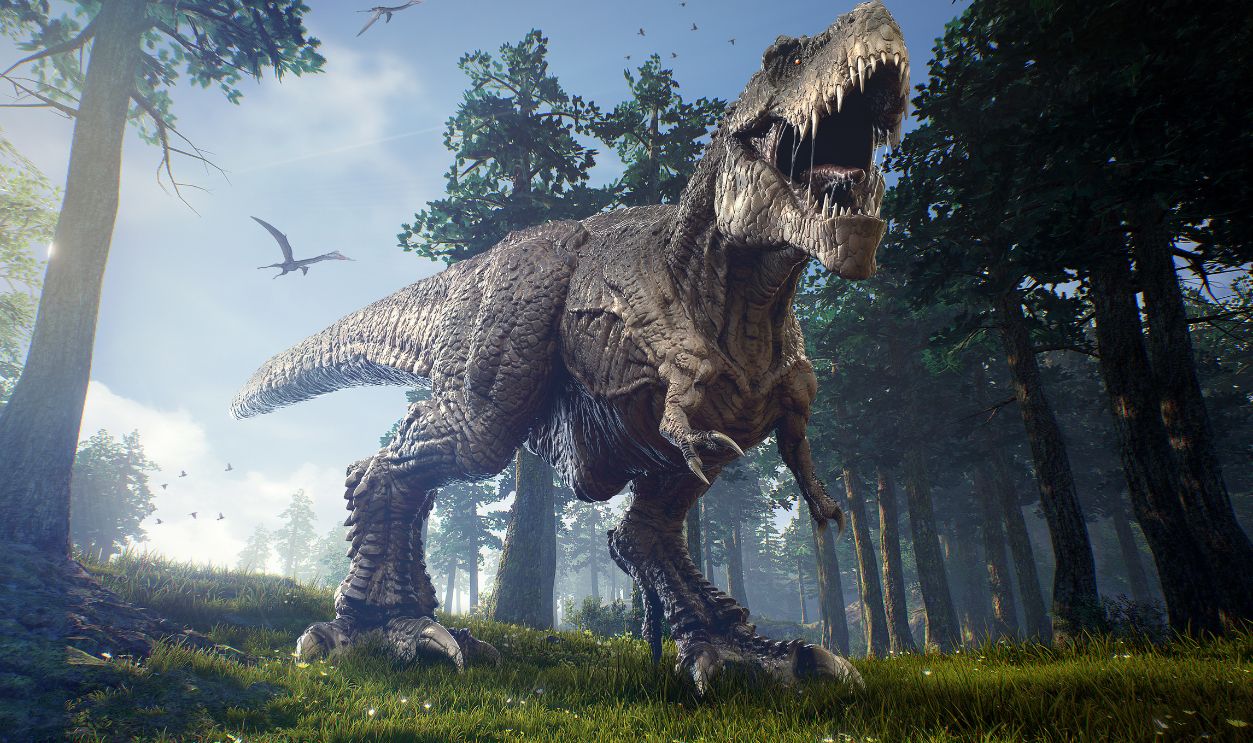
From Single-Celled Organisms To Dinosaurs
The idea of Deep Time has to do with everything about life and its journey, from single-celled organisms to the giant ever-feared dinosaurs like T. rex. Sequoia just takes us back and opens our minds to the types of life that once existed in our absence.
 Herschel Hoffmeyer, Shutterstock
Herschel Hoffmeyer, Shutterstock
A Journey Through Vast Time
The sequoia tree gives us a clue into a world that is out of human order. Although it lived for 260 years, it dates back 16 million years. This connects us to the ancient world farther than the one our great-grandparents ever walked on.
 Lucky-photographer, Shutterstock
Lucky-photographer, Shutterstock
Millions Of Lifetimes Encapsulated
Sequoia’s existence can be said to be 200,000 human lifetimes, showcasing Earth's deep geological timeline. The rings that it preserved are a reminder of the planet's deep history, which allows us to reflect on our short presence within this vast continuum of time.
 Jeison Jaramillo, Shutterstock
Jeison Jaramillo, Shutterstock
Unveiling Earth's Transformation
Over millions of years, Earth has witnessed countless transformations. Thanks to the sequoia, we can trace a line from the ancient environments that once thrived to those of the modern human era.
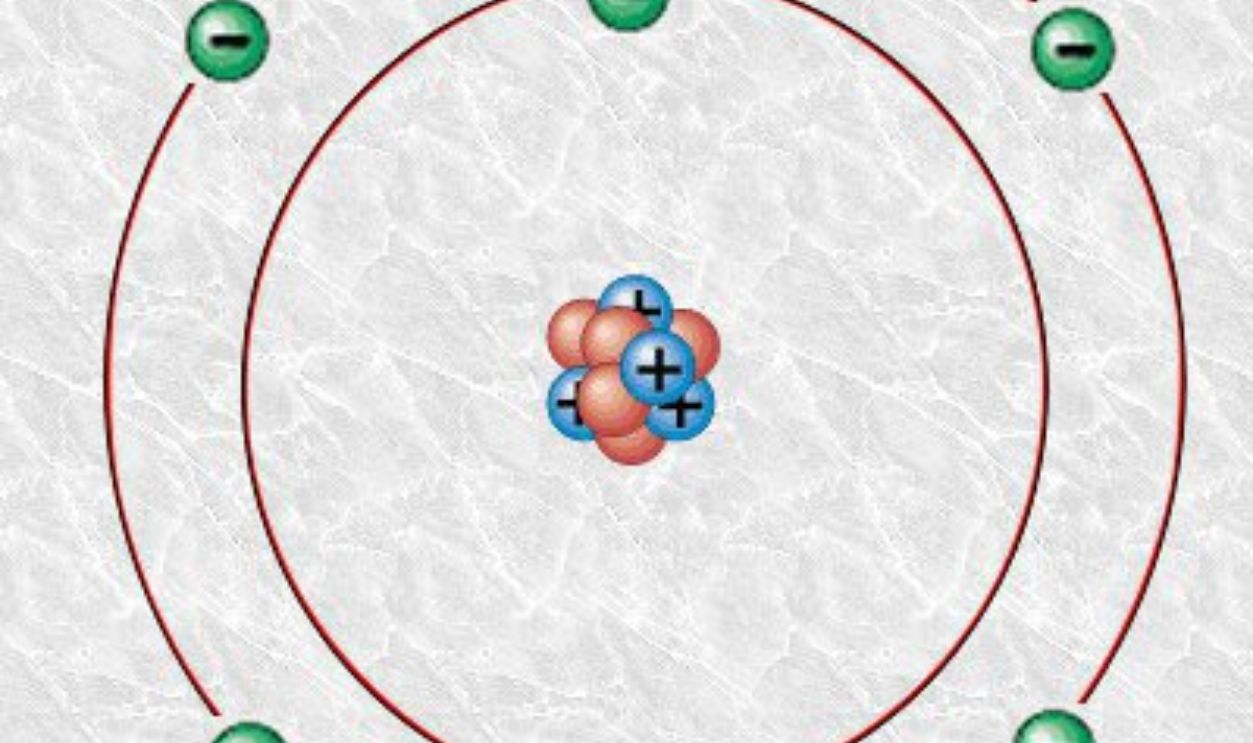
What We Learn From Carbon Atoms
As we begin to wrap, let's briefly share our takeaways. The carbon atoms in this tree give us a peek into what the air was like 16 million years ago. These atoms are trapped in the tree, and by studying them, scientists are learning about the past and how it connects to the present.
 Alejandro Porto, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Alejandro Porto, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Our Place In Earth's Story
In conclusion, there are many things that existed before humans on this Earth, and to preserve them, we need to study the lives of those who were the first occupants. For example, the ancient sequoia offers a profound lesson about the continuity of life.






















